
DENTALADMISSION TESTING
PROGRAM
Sample Test Items
DentalAdmission Testing Program
211 East ChicagoAvenue, Suite 600
Chicago, Illinois 60611
1-800-232-2162
American DentalAssociation
www.ada.org
®
These sample test items are reprinted for distribution in 2007 by the American Dental Association.
© 2007 American Dental Association. All rights reserved.
You may not reproduce or transmit, by any means or for any purpose, this publication, or any part
of it, in print, electronic or other format without prior express written permission from the
American Dental Association.

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
DENTAL ADMISSION TEST PREPARATION MATERIALS
How does one prepare for the DAT? There are no shortcuts to the process of learning, and these test
preparation materials are not designed to provide the applicant with an opportunity to bypass the extensive
process of absorbing basic information through class participation and months of study. These test
preparation materials contain samples of the four tests used in the Dental Admission Testing Program.
These are available to DAT applicants as a means of discovering possible areas of weakness in their
comprehension of subjects covered by the test. They will also enable the candidates to become familiar
with the types of material included in the test as well as with the general coverage and format of the various
parts of the test battery.
The entire DAT takes 4 hours and 45 minutes (including a 15-minute optional tutorial and break). In the real
DAT, the time limit will be indicated in the upper right hand corner on the computer screen. Therefore, you
will need to pace yourself as you proceed through each test in the Dental Admission Test. If you have time
remaining for a section of the test, you can review your responses. When time expires, the computer
screen will move to the next test or optional break period. The structure of the test is given below.
You are encouraged to review the DAT Tutorial at www.ada.org/dat.aspx under Step 4 before taking the
actual DAT. The tutorial provides some sample items and information on navigating through the test.
The Survey of the Natural Sciences is a test of achievement. The content is limited to those areas
covered by an entire first-year course in biology, general chemistry, and organic chemistry. The examination
is comprised of 100 items: 40 biology items, 30 general chemistry items, and 30 organic chemistry items.
Since separate sub-scores will be given for each of the three science sections, you should pace yourself
through each section. A periodic table is available in the front of the Sample Test Items booklet and will be
available as an Exhibit button on the actual DAT.
The Perceptual Ability Test includes various types of nonverbal visual acuity items. There are six sections
to the Perceptual Ability Test. One section covers two-dimensional perception, while the other sections
cover three-dimensional perception. It is important that you read and understand the instructions at the
beginning of each section. You must pace yourself so that you complete all six sections of the Perceptual
Ability Test within the given time frame. You are not permitted to use measuring devices (i.e., pencils and
fingers) while taking the Perceptual Ability Test.
The Reading Comprehension Test consists of three reading passages, each with 16 to 17 items. The
reading passages are scientific in nature and may reflect topics covered in dental school. Candidates are
encouraged to read each passage before attempting to answer the corresponding questions. On the actual
DAT, the Reading Comprehension Test is presented in a split-screen format with the items presented on the
upper half of the screen, while the reading passage is presented in a scrollable format on the lower half of
the screen. One reading passage is provided in the Sample Test Items.
The Quantitative Reasoning Test measures your ability to reason with numbers, to manipulate numerical
relationships, and deal intelligently with quantitative materials. On the actual DAT, a basic calculator will be
available as a pop-up image for the Quantitative Reasoning Test only.
Dental Admission Test
Components of the Test Number of Items Time Allowance
Optional Tutorial 15 minutes
Survey of the Natural Sciences 100 90 minutes
Perceptual Ability Test 90 60 minutes
Optional Break 15 minutes
Reading Comprehension Test 50 - across three reading passages 60 minutes
Quantitative Reasoning Test 40 45 minutes

PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS
© 2000 American Dental Association. All rights reserved.

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
1
1. Organisms that obtain their energy from
light can be termed
A. autotrophic.
B. holotrophic.
C. chemotrophic.
D. heterotrophic.
E. heliotrophic.
2. Fermentation
A. produces pyruvic acid as an end
product.
B. yields less energy per mole of
glucose than aerobic respiration.
C. occurs only in the presence of
oxygen.
D. prevents glycolysis from occurring.
E. converts ethanol to glucose.
3. In respiration, oxygen
A. combines with lactic acid to form
pyruvic acid.
B. acts as a cofactor for glycolytic
enzymes.
C. yields energy in the form of ATP as
it is passed down the respiratory
chain.
D. acts as an acceptor for electrons
(and protons), forming water.
E. combines directly with carbon,
forming CO
2
.
4. An enzyme is added to an aqueous
solution of ATP, DNA, albumen, fat and
glycogen; the reaction mixture is
incubated for 10 minutes. If an analysis of
the mixture reveals the presence of all of
the above compounds plus glucose, it
can be concluded that the enzyme
hydrolyzed some of the
A. albumen.
B. fat.
C. glycogen.
D. ATP.
E. DNA.
5. What cellular organelles would you
expect to be absent from fungi?
A. Mitochondria
B. Lysosomes
C. Ribosomes
D. Golgi bodies
E. Chloroplasts
6. Intracellular organelles that participate in
metabolic oxidations involving H
2
O
2
are
called
A. centrioles.
B. endoplasmic granules.
C. peroxisomes.
D. lysosomes.
E. macrobodies.
This examination is comprised of 100 items:
Biology (1-40), General Chemistry (41-70), and Organic Chemistry (71-100)

7. The two daughter cells formed by mitosis
and cytokinesis have
A. half the number of chromosomes
present in the parent cell.
B. half the number of the
chromosomes present in the parent
cell if this parent cell is found in the
testicular or ovarian tissue.
C. the same number of chromosomes
present in the parent cell.
D. twice the number of chromosomes
present in the parent cell.
E. a variable number of chromosomes
so that an exact prediction cannot
be made.
8. Starch, cellulose and glycogen are all
A. proteins.
B. linked internally by hydrogen
bonds.
C. water soluble.
D. polymers of glucose.
E. nucleic acids.
9. Each of the following cell organelles have
a membranous structure EXCEPT one.
Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A. Golgi complex
B. Centrioles
C. Mitochondria
D. Lysosomes
E. Endoplasmic reticulum
10. In anaerobic glycolysis in muscle cells,
one mole of glucose is oxidized to
A. six moles of carbon dioxide.
B. two moles of acetic aid.
C. two moles of lactic acid.
D. two moles of acetyl CoA.
E. two moles of carbon dioxide and six
moles of water.
11. The movement of water soluble
molecules through cell membranes, from
higher to lower concentrations, by
attachment to a carrier protein, describes
A. diffusions.
B. osmosis.
C. pinocytosis.
D. active transport.
E. facilitated diffusion.
12. As far as their products are concerned,
all biosynthetic reactions in living cells
result in
A. a more ordered state, therefore a
decrease in entropy.
B. a more ordered state, therefore an
increase in entropy.
C. energy released in the form of ATP.
D. energy made available for motion.
E. a more ordered state with no
entropy change.
13. Which is the smallest organelle in the
cell?
A. Golgi body
B. Nucleus
C. Mitochondrion
D. Ribosome
E. Chloroplast
14. For a given diameter of an axon, one
factor which increases the velocity of a
nerve impulse is
A. the length of the axon.
B. the ploidy of the nucleus.
C. the density of mitochondria along
the axon.
D. maximal stimulation of the neuron.
E. the presence of a myelin sheath.
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
2

15. Which chiefly stimulates action of the
respiratory center?
A. Carbon dioxide in the blood
B. Relaxin
C. Lack of oxygen in the blood
D. Inflation of the alveolus
E. Vagus nerve
16. The term motor unit refers to
A. an entire muscle.
B. a single muscle fiber.
C. all the muscle fibers innervated by
one nerve fiber.
D. all the motor nerves in one muscle.
E. all the sliding filaments of actin and
myosin in one muscle fiber.
17. The human heart beat is initiated within
the
A. sinus venosus.
B. Hensen’s node.
C. conus arteriosus.
D. artio-ventricular node.
E. sino-atrial node.
18. In the nephron of the kidney, filtration
occurs between
A. Bowman’s capsule and Henle’s
loop.
B. the glomerulus and Bowman’s
capsule.
C. the proximal tubule and Henle’s
loop.
D. Henle’s loop and the vasa recta.
E. the peritubular network and the
convoluted tubules.
19. The addition of potassium iodide as a
nutritional supplement to common table
salt would most directly affect the function
of which of these glands?
A. Thyroid
B. Sweat glands
C. Adrenal cortex
D. Kidneys
E. Parathyroid
20. Each of the following is synthesized by
the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland of
vertebrates EXCEPT one. Which one is
the EXCEPTION?
A. Thyrotropic hormone
B. Adrenocorticotropic hormone
C. Follicle-stimulating hormone
D. Growth hormone
E. Oxytocin
21. Clotting of human blood
A. requires that hemoglobin be
present.
B. results from fibrin joining globulin.
C. is a result of platelets releasing
fibrinogen.
D. depends on the formation of fibrin
from fibrinogen.
E. is accelerated when Ca
2+
is
removed.
22. At some stage of development, all
chordates have
A. a pharynx, a vertebral column, and
a notochord.
B. pharyngeal pouches, a notochord,
and a dorsal tubular nerve cord.
C. pharyngeal pouches, a notochord,
and a ventral nerve cord.
D. pharyngeal pouches, vertebral
column, and a dorsal tubular nerve
cord.
E. a pharynx and an ectodermally
derived, solid nerve cord.
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
3

23. Organisms that have the characteristics
of radial symmetry, water vascular
system, a spiny skin, and are found
exclusively in a marine habitat would be
in which phylum?
A. Annelida
B. Chordata
C. Cnidaria
D. Porifera
E. Echinodermata
24. Of the following, which group of
invertebrates is apparently most closely
related to primitive vertebrates?
A. Annelida
B. Mollusca
C. Cnidaria
D. Arthropoda
E. Echinodermata
25. Under the five-kingdom classification,
members of the kingdom Monera are
generally separated from the members of
all the other kingdoms by having
A. heterotrophic nutrition versus
autotrophic nutrition.
B. unicellular organization versus
multicellular organization.
C. microscopic size versus
macroscopic size.
D. prokaryotic cells versus eukaryotic
cells.
E. parasite-host relationship versus
predator-prey relationship.
26. A segment of DNA with the sequence
GGCATTAGG would be transcribed into a
messenger RNA segment with the
sequence
A. CCGUAAUCC.
B. AATGCCGTT.
C. CCGTAATCC.
D. AAUGCCGUU.
E. CCGTUUTGG.
27. Assuming no linkage, how many different
kinds of gametes can be produced by an
organism with the genotype AaBbcc?
A. 32
B. 16
C. 8
D. 6
E. 4
28. Which statement concerning alleles is
true for diploid organisms?
1. At most only two alleles occur at a
given locus in an organisms
genome.
2. Alleles occupy an identical locus in
homologous chromosomes.
3. Alleles of a given gene usually
occur on non-homologous
chromosomes.
4. A single chromosome usually
carries two alleles of each gene.
A. 4
B. 1 and 2
C. 3
D. 1, 2 and 4
E. 3 and 4
29. In watermelons, the unlinked genes for
green color (G) and for short length (S)
are dominant over alleles for striped color
(g) and long length (s). Predict the
phenotypes and their ratios for the cross
Ggss x ggSs.
A. All green short
B. 1:2:1 green short: striped long:
striped short
C. All striped long
D. 1:1:1:1 green short: striped short:
green long: striped long
E. 1:1 green short: striped long
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
4

30. Sexual and asexual reproduction usually
differ in
A. the ability of the new offspring to
reproduce.
B. the rate at which mutations occur.
C. the amount of genotypic variation
between parent and offspring.
D. the viability of offspring.
E. whether or not natural selection can
occur.
31. In human beings, color blindness is
controlled by an X-linked recessive allele.
In a cross involving this X-linked trait, the
male parent has normal color vision, but
the female parent is a carrier. What are
the chances (in %) that a male offspring
will inherit color blindness?
A. 10
B. 25
C. 50
D. 75
E. 100
32. Consider a pair of homologous human
chromosomes. In this pair one would
expect
A. them to be genetically identical.
B. one chromosome to carry dominant
alleles and the other recessive
alleles.
C. one chromosome to have been
inherited from the mother and the
other from the father.
D. the two chromosomes to synapse
during mitotic prophase.
E. them to have different shapes.
33. Embryonic induction is a process in
which
A. embryonic tissues influence
adjacent tissues to differentiate.
B. an unfertilized egg is induced to
develop.
C. genes are transferred from one
developing tissue to another.
D. resting potentials are induced in
neurons of embryos.
E. the maternal parent induces
expression of recessive genes in
embryos.
34. Which statement is true of the
archenteron?
A. The cavity of the archenteron is
called the blastocoele.
B. The cavity of the archenteron
represents the beginning of the
primitive gut.
C. The archenteron is formed during
blastula formation.
D. The cavity of the archenteron
represents the first cavity of the
developing heart.
E. The archenteron is formed by a
closing of the neural tube.
35. Of the germ layers comprising the early
human embryo, which one forms most of
the central nervous system?
A. Ectoderm
B. Mesoderm
C. Endoderm
D. Notochord
E. Dermis
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
5

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
6
36. Of the following, the rate and type of
cleavage occurring after fertilization
would be most affected by the
A. amount and distribution of yolk.
B. number of chromosomes.
C. thickness of the cell membrane.
D. temperature.
E. thickness of the zona pellucida.
37. The long-term natural process by which a
pond eventually becomes a terrestrial
community is referred to as
A. environmental disruption.
B. habitat development.
C. organic evolution.
D. ecological succession.
E. desertification.
38. The initial step in the speciation process
often involves
A. inbreeding within the species.
B. geographical separation of
populations.
C. intraspecific-random mating.
D. the inheritance of acquired
characteristics.
E. a Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
39. A complex behavioral response to a
specific cue or releaser, which is
exhibited by all members of the species
as a stereotyped response to the same
stimulus, is known as a
A. conditioned response.
B. fixed-action pattern.
C. reflex.
D. kinesis.
E. taxis.
40. Each of the following changes the
frequency of alleles in a population
EXCEPT one. Which one is the
EXCEPTION?
A. Mutation
B. Natural selection
C. Immigration
D. Random interbreeding
E. Genetic drift
41. A 49-gram sample of sulfuric acid,
H
2
SO
4
(98 g
!mol
-1
) contains
A. 1 mol of S atoms.
B. 16.0 grams of O.
C. 2.0 grams of H.
D. 2 moles of O atoms.
E. 1 mole of molecules.
42. If 1 mole of N
2
and 1 mole of H
2
are
mixed and allowed to react according to
the equation N
2
+ 3H
2
2NH
3
. What
is the maximum number of moles of NH
3
that could be produced?
A. 2/3
B. 3/2
C. 2/1
D. 1/2
E. 1/1
43. A flask weighs 95 g when empty. When
filled with 200 mL of a certain liquid, the
weight is 328 g. What volume (in
milliliters) would 1,000 g of the liquid
occupy?

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
7
44. If 3.00 g of a nitrogen-oxygen compound
is found to contain 2.22 g of oxygen, what
is the percentage of nitrogen in the
compound?
45. A 10.0 liter sample of oxygen at 100°C
and 1 atm is cooled to 27°C and
expanded until the pressure is 0.5 atm.
Find the final volume of the oxygen.
46. When the volume of a gas is decreased
at constant temperature, the pressure
increases because the molecules
A. move faster.
B. move slower.
C. become heavier.
D. become lighter.
E. strike a unit area of the container
more often.
47. Water has a higher boiling point than
compounds of a similar molecular weight.
Which best explains this phenomenon?
A. Extensive hydrogen bonding exists
between water molecules.
B. One of the natural isotopes of
hydrogen, deuterium, is present in
sufficient quantities to significantly
raise the boiling point.
C. Water is a polar covalent
compound.
D. Van der Waals forces exist between
individual water molecules.
E. Water is largely dissociated leading
to large electrostatic forces
between individual water
molecules.
48. A substance is non-conducting as a solid
and melts at 750°C. The melt conducts
electricity. The solid is observed to be
soluble in water. This substance would be
best classified as
A. molecular.
B. ionic.
C. macromolecular.
D. metallic.
E. polymeric.

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
8
49. How many grams of NaOH (40 g!mol
-1
)
are there in 250 mL of 0.4 M NaOH
solution?
A. 0.1
B. 0.4
C. 4
D. 10
E. 40
50. Which will be the final volume when 400
mL of 0.6 M HCl is diluted to 0.5 M HCl?
51. During a titration it was determined that
30.00 mL of a 0.100 M Ce
4+
solution was
required to react completely with 20.00
mL of a 0.150 M Fe
2+
solution. Which
reaction occurred?
A. Ce
4+
+ 3Fe
2+
+ H
2
O 3Fe
3+
+ CeO
-
+ 2H
+
B. 2Ce
4+
+ Fe
2+
Fe
4+
+ 2Ce
3+
C. Ce
4+
+ Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ Ce
3+
D. Ce
4+
+ 2Fe
2+
2Fe
3+
+ Ce
2+
E. Ce
4+
+ 2Fe
2+
2Fe
4+
+ Cs
2+
+ 2e
-
52. If 25 mL of 0.5 M NaOH neutralizes
35 mL of a monoprotic acid, which
is the molarity of the acid?
53. In which reaction is H
2
O considered to
be acting as an acid?
A. Zn(s) + 2H
3
O
+
Zn
2+
+ H
2
(g)
+ H
2
O
B. HCl(g) + H
2
O H
3
O
+
+ Cl
-
C. HC
2
H
3
O
2
+ H
2
O H
3
O
+
+
C
2
H
3
O
2
-
D. NH
3
+ H
2
O NH
4
+
+ OH
-
E. NH
3
+ H
3
O
+
NH
4
+
+ H
2
O
54. At constant temperature when the
following reactions involving gases are at
equilibrium, which reaction shifts to the
right if the pressure is increased?
A. 2H
2
+ O
2
2H
2
O
B. 2NH
3
N
2
+ 3H
2
C. 2SO
3
2SO
2
+ O
2
D. 2NO N
2
+ O
2
E. 2CO
2
2CO + O
2

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
9
55. For the equilibrium
Ag
2
SO
4
(s) 2Ag
+
(aq) + SO (aq)
The solubility product expression (K
sp
) is
A. 2[Ag
+
][SO ]
B. [Ag
+
][SO ]/[Ag
2
SO
4
]
C. [Ag
+
][SO ]
D. 2[Ag
+
]
2
[SO ]/[Ag
2
SO
4
]
E. [Ag
+
]
2
[SO ]
56. The concentrations of silver ion and
chloride ion in an aqueous solution in
equilibrium with solid silver chloride are
1.0 x 10
-6
M. What is the value of K
sp
for
AgCl equal to?
A. (2.0 x 10
-6
)(1.0 x 10
-6)
B.
C. 1.0 x 10
-6
D. 1(1.0 x 10
-6
)
E. (1.0 x 10
-6
)
2
57. Determine the heat in kcal/mol available
from the oxidation of one mole of glucose
(C
6
H
12
O
6
).
C
6
H
12
O
6
(s) + 6O
2
(g) 6CO
2
(g) +
6H
2
O(1)
The heats of formation are:
Substance
∆∆
H , kcal/mol
C
6
H
12
O
6
(s) -297
CO
2
(g) -94
H
2
O(l) -68
A. -94 - 68 - 297
B. 6(-94) + 6(-68) + 1(-297)
C. 6(-94) + 6(-68) - 1(-297)
D. 1(-297) - 6(-94) - 6(-68)
E. 297 - 94 - 68
58. Which process is accompanied by a
decrease in entropy?
A. Sublimation of carbon dioxide
B. Evaporation of water
C. Freezing of water
D. Shuffling a deck of cards
E. Heating a balloon filled with a gas
59. If a solution which is 0.50 M in compound
X decomposes for 5.0 minutes at an
average rate of 0.040 M
!min
-1
, the new
concentration of X will be
A. 0.04 M.
B. 0.05 M.
C. 0.20 M.
D. 0.30 M.
E. 0.50 M.
2-
4
2-
4
2-
4
2-
4
2-
4
2-
4
o
f

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
10
60. For the reaction A + B C, the
experimentally determined rate of
formation of C is given by:
Rate = k[A][B]
2
. Doubling the
concentration of B will
A. quadruple the initial reaction rate.
B. double the initial reaction rate.
C. have no effect on the initial rate.
D. halve the initial reaction rate.
E. reduce the rate to one-fourth its
initial value.
61. The following is a spontaneous oxidation-
reduction reaction:
Cr
2
O + 14H
+
+ 6I
-
2Cr
3+
+7H
2
O + 3I
2
Which is the best reducing agent?
A. Cr
2
O
B. H
+
C. I
2
D. H
2
O
E. I
-
62. Given the following half-cell reactions:
Cl
2
(g) + 2e
-
2Cl
-
(aq) E°= +1.36v
Cu
2+
(aq) + 2e
-
Cu(s) E°= +0.34v
What is the value of E° for the following
reaction?
Cu
2+
(aq) + 2Cl
-
(aq) Cu(s) + Cl
2
(g)
A. -2.38v
B. -1.70v
C. -1.02v
D. +1.02v
E. +1.70v
63. In which two compounds does nitrogen
have the same oxidation number?
A. N
2
O
3
and HNO
3
B. N
2
O
5
and HNO
3
C. NO
2
and N
2
O
3
D. N
2
O
4
and HNO
2
E. HNO
2
and NH
3
64. Which species is linear?
A. H
2
O
B. H
2
Se
C. SO
2
D. ClO
2
E. CO
2
65. The three common isotopes of oxygen:
16
O,
17
O,
18
O, have
A. the same atomic number and an
equal number of protons.
B. the same mass number and an
equal number of neutrons.
C. the same atomic number and an
equal number of neutrons.
D. the same mass number and an
equal number of protons.
E. the same mass number and an
equal number of electrons.
2-
7
2-
7
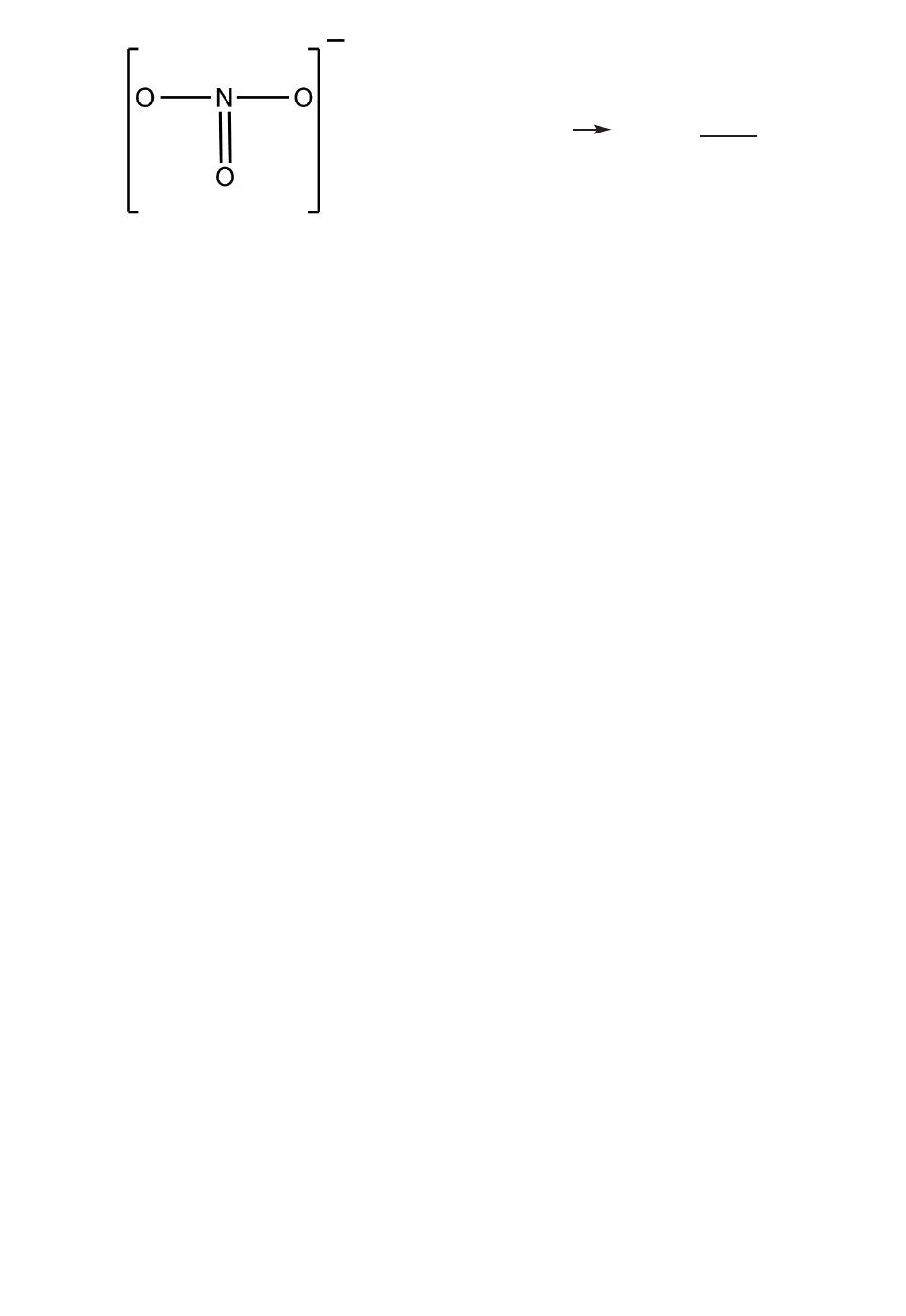
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
11
66. A Lewis structure for the NO
-
3
ion is
Including this structure, the total number
of ground state resonance structures for
this ion is
A. 1.
B. 2.
C. 3.
D. 4.
E. 5.
67. The electronic configuration of a
particular neutral atom is
1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
2
. What is the number of
unpaired electrons in this atom?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 0
68. Which property increases with atomic
number among the representative
elements of period two?
A. Atomic radius
B. Electronegativity
C. Metallic character
D. Normal boiling point
E. Melting temperature
69. Which pair would give the bond with the
most ionic character?
A. Al and S
B. P and O
C. B and Br
D. C and S
E. Li and O
70. In the reaction shown below a nitrogen
nucleus containing six neutrons emits a
positron. What is the second product of
the balanced reaction?
N e +
A. N
B. N
C. C
D. C
E. O
71. A characteristic feature of the S
N
2
reaction mechanism is that
A. it follows first-order kinetics.
B. it produces stereochemical
inversion of configuration.
C. there is no rate-determining step.
D. steric factors have little influence on
the reaction rate constant.
E. collision of three or more particles
is required.
13
7
0
+1
13
7
14
7
14
6
13
6
13
8

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
12
72. Which alkyl bromide will most readily
undergo S
N
2 reaction with NaOH?
73. Ethane reacts with chlorine in the pres-
ence of heat or ultraviolet light to give
chloroethane.
CH
3
CH
3
+ Cl
2
CH
3
CH
2
Cl + HCl
Which is an intermediate in this reaction?
74. How does the energy content of the
transition state of a chemical reaction
compare with that of the reactants and
products?
A. It is greater than products but less
than reactants.
B. It is greater than reactants but less
than products.
C. It is equal to both reactants and
products.
D. It is less than both reactants and
products.
E. It is greater than both reactants and
products.
75. Which intermediate is most likely to be
involved in the reaction shown below?
CH
3
CH=CHCH
3
+HCl CH
3
CH
2
CHCH
3
heat or
UV light
Cl

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
13
7
6.
77. A strong infrared absorption band
between 1,750 and 1,700 cm
-1 (5.71-
5.88
µ
)
indicates the presence of
78. If partitioned between equal volumes of
ether and water, which would show the
greatest preference for the water layer?
A. CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
B.
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
Cl
C. CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
OH
D. HO CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
OH
E. HO CH
2
CH CH CH CH
2
OH
79. Which structure below is an important
resonance form of
OH OH OH

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
14
80. Which of the structures below is chiral?
81. What are the following?
A. Structural isomers
B. Enantiomers
C. Diastereomers
D. Identical compounds
E. Meso compounds
82. Which conformation of
1, 4- dibromocyclohexane is the most
stable?

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
15
83. Which structure represents a trans (E)
isomer?
84. Which is the IUPAC name for this
compound?
A. 4-methyl-l-hexene
B. 4-ethyl-1-pentene
C. 2-ethyl-4-pentene
D. sec-butyl propylene
E. 3-methyl-5-hexene
85. The reduction of a ketone
A. an aldehyde first, then a primary
alcohol.
B. a primary alcohol.
C. a secondary alcohol.
D. a tertiary alcohol.
E. a carboxylic acid.
86. What is the major product of the following
reaction?

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
16
87. In the reaction,
the major product is
88. The reaction of CH
3
CH
2
MgBr with
CH
3
CCH
3
followed by hydrolysis with
dilute aqueous acid gives
89. Which reaction is an example of a free
radical chain termination step?
90. What is the product of the reaction shown
below?
O

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
17
91. Which could be used in the following
conversion?
A. LiAlH
4
B. CrO
3
, H
+
C. SOCl
2
D. PBr
3
E. H
3
O
+
92. Which of the alkenes shown below reacts
with ozone to give the products shown?
93. The two Bronsted-Lowry bases in the
equilibrium below are
HOAc + NaCN HCN + NaOAc
A. HoAc + NACN
B. HOAc + NaOAc
C. NaCN + NaOAc
D. NaCN + HCN
E. HOAc + HCN
94. The most acidic type of hydrogen in the
following compound is
A. a
B. b
C. c
D. d
E. e

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
18
95. The conjugate acid of p-aminophenol 96. The structure below is shown without
complete geometrical detail. What is the
correct assignment of bond angles?
A. a = 90° b = 90°
B. a = 180° b = 109.5°
C. a = 120° b = 120°
D. a = 180° b = 120°
E. a = 180° b = 180°
97. Which is stabilized by resonance?

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
19
98. Which of the following is aromatic? 99. Treatment of benzoic acid with thionyl
chloride followed by addition of ethanol
gives which as the major product?

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
20
100. What is the final product (B) of the
sequence below?

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
24

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
25

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
26

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
27

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
28

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
29

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
30

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
31

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
32

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
33

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
34

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
35

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
36

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
37

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
38

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
39

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
40

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
41

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
42

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
43

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
44

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
45

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
46

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
47

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
48

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
49

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
50

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
51

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
1
IONIZING RADIATION:
RISK AND BENEFIT
X radiation is a form of energy which was
discovered by the German physicist, Wilhelm
Conrad Roentgen in 1895. Like visible light,
radiowaves, and microwaves, X-rays belong
to a group of radiations known as the electro-
magnetic spectrum. Electromagnetic
radiations are comprised of units of pure
energy called photons or quanta. Unlike
corpuscular, or particular, radiations which are
composed of subatomic particles, electro-
magnetic radiations have no mass or weight.
Subatomic particles that can be involved in
corpuscular radiations include the alpha
particle or helium radical, the beta particle or
electron, neutrons and protons. Corpuscular
radiations can cause ionization; however, for
the purposes of the present discussion only
electromagnetic radiations capable of causing
ionization will be considered.
All photons of electromagnetic radiation travel
in direct lines in a wave motion at the speed
of 300,000 kilometers per second. Many of
our conceptual ideas about wave motion are
the result of our sensory experience with the
transverse waves which occur in water and in
the stretched string of a musical instrument. It
is a pity in some way that the same term,
wave, is given to both this transverse wave
form and the oscillatory movement which is
propagated along the direction of travel by
electromagnetic radiations. This oscillatory
movement, or longitudinal wave propagation,
can be seen when a coiled spring is tapped
sharply at one end, and as such this is a good
paradigm for electromagnetic wave motion.
Whereas for transverse waves the wavelength
is between successive crests, the wavelength
for electromagnetic radiations is the distance
between successive areas of compression.
This distance can vary enormously and
electromagnetic radiations of different
wavelengths have different properties. At one
end of the spectrum there are very long
wavelengths. Electromagnetic radiation of
long wavelength is used in the transmission of
radio messages. At the other end of the
spectrum are the short wavelength radiations
such as gamma radiations, which arise from
naturally occurring unstable elements, and X-
rays which are similar in property to gamma
radiations, but are man-made by bombarding
a target material with electrons in an X-ray
tube. For gamma and x radiations the
wavelengths are so small that they are
measured in Angstrom units, where an
Angstrom unit is 1/100,000,000 centimeter.
The shorter the wavelength, the higher the
energy and penetrating power of the photon,
and (as all electromagnetic radiations travel at
the speed of light) the higher the frequency of
waves. X-ray wavelengths used in diagnostic
radiology range from approximately 0.1 to 0.5
Angstroms. At such wavelengths the radiation
has sufficient energy to cause ionization of
atoms and molecules. If such atoms or
molecules are within living systems, there is
the potential for biological harm. This is the
reason for the paradox that X-rays can cause
cancer, can be used to help in diagnosis of
disease, and in high doses can be used to
destroy cancer cells.
Consideration of the potential benefits of an
activity is involved in the decision of risk
acceptability. In diagnostic radiology, the risk-
benefit equation is difficult to estimate. Risk is
generally given in units of equivalent radiation
dose, while the benefit is expressed in such
terms as saved or disease cured. Gibbs and
his fellow workers have noted that estimates
of risk whole-body exposure, which is not
generally the case for the diagnostic use of
Reading Comprehension Test Time limit: 15 minutes
RCT - Test Number 52
(Actual Test will contain three passages and
the time limit will be 60 minutes)

x radiation. Moreover, they indicated that it has
not yet been possible to define the value of a
life saved in units of dose equivalence.
Because of these uncertainties, diagnostic
radiation is to be regarded as a potentially
noxious agent. Hence radiological examination
should be carried out only if it is likely that the
information obtained will be useful for the
clinical management of the patient.
Undoubtedly ionizing radiation in high doses
can be harmful. The first report of patient injury
from a diagnostic radiological procedure,
namely skin burns, was made within a few
months of Roentgen’s discover of the X-ray. In
that case the exposure time was one hour, but
it is impossible to estimate the dose received.
As early as 1902 the first case of cancer
attributed to radiation injury was reported in the
literature. Nonetheless, the magnitude of the
risk (or even if there is a risk) from the small
doses of x radiation presently employed for
diagnostic purposes is still undetermined.
Various accidents, such as the recent reactor
incident at Chernobyl in the Soviet Union,
knowledge gained from follow-up studies on
survivors from the atom bomb explosions in
Hiroshima and Nagasaki at the end of World
War II, and experiments subjecting various
plant and animal species to ionizing radiation
indicate that radiation bioeffects can be divided
into two basic types where relatively high doses
of radiation are concerned. One category of
effects requires a threshold dose can be met
before detectable change occurs. Such effects
are termed non-stochastic, and are primarily a
result of cell death. Examples are the acute
radiation syndrome and the development of
cataracts. On the other hand, stochastic effect
show statistical probability of occurrence as a
function of dose, but no threshold cut off for the
effect. Examples of stochastic effects are
carcinogenesis and genetic mutations.
The problem in evaluating the risk of cancer or
mutation in human populations due to the
diagnostic use of x radiation is that there is no
known method to distinguish between disease
resulting from the radiation and that which is
spontaneous or due to other factors in
environment. The only way to assess the
magnitude of the risk would be to determine the
excess incidence of cancer or mutations in an
irradiated population. Where the excess
incidence is expected to be small, extremely
large populations and long periods of
observation are required. Land, for example,
suggested that the risk of breast cancer from
mammography is numerically so small when
compared to the spontaneous incidence of one
in 13 for breast cancer in U.S. women, that the
epidemiologic methods of evaluation would
require a population of at least 60 million
women followed from age 35 until death. Half
of them would receive mammograms and the
other half, the control group, would not. It goes
without saying, that such a study would take at
least 40 years to conduct and would be so
prohibitively expensive that it is not likely to be
carried out. Similar considerations apply to the
evaluation of risks from small doses of ionizing
radiation of all human cancers and mutations.
Hence, it has been common practice to use
quantitative estimates and interpolations from
observations of human and animal populations
exposed to large radiation doses, when
attempting to make numeric estimates of the
risks to humans from low doses of ionizing
radiation.
In view of the uncertainty surrounding possible
risks from the diagnostic use of X-rays, the
International Commission on Radiological
Protection has originated the concept of
keeping exposure levels “as low as reasonably
achievable.” This concept has been
summarized in cryptic acronym form as the
ALARA Principle. The three key ways of
minimizing exposure to radiation are minimizing
the duration of exposure, maximizing the
distance from the source, and using barriers
such as leaded clothing or screens. Diagnostic
X-ray production occurs only when the X-ray
tube is energized, and this is only necessary
when radiographs are being exposed. The time
that the X-ray tube is energized can be
reduced by using fast image receptors, and by
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
2

reducing the number of radiographs taken by
high-yield selection criteria of the exposures to
be performed. As the intensity of the X-ray
beam is inversely proportional to the square of
the distance from the source (e.g. when the
distance is doubled the intensity of the beam is
reduced by a factor of four, when tripled it is
reduced by a factor of nine…) the operation
should be as far as possible to stand behind a
barrier impregnable to the X-rays being used.
By conscientious use of ALARA Principle, the
practitioners reduce risks for themselves, their
staff and their patients.
1. Which was the earliest descriptor of ill
effects attributed to x radiation?
A. Cancer in atom bomb survivors
B. Genetic mutations following
mammography
C. Radiation burns due to prolonged
exposure
D. Acute radiation syndrome after the
Chernobyl incident
E. Cataracts
2. Of the following, which is the electro-
magnetic radiation having the longest
wavelength?
A. Gamma radiation
B. Alpha radiation
C. Beta radiation
D. X radiation
E. Radiowave radiation
3. From statements in the passage, it can be
inferred that the author probably
is a(n)
A. sentimentalist whose judgments are
influenced primarily by his emotions.
B. skeptic who refuses to believe
anything without absolute proof.
C. realist who adheres to practical
considerations and rejects the
impractical.
D. idealist who places his own
standards of perfection before
practical matters.
E. conformists who follows the ideas of
authority without question.
4. Wave motion for x radiation most closely
resembles the oscillating movement of a
A. fast-moving helium radical.
B. coiled spring that has been sharply
tapped at one end.
C. plucked stretched string of a musical
instrument.
D. Wave in water caused by
disturbance from a fast moving motor
boat.
E. transverse wave form.
5. The paradox of x radiation is stated to
be that
A. it is used for diagnostic purposes
when the risks involved have not
been fully determined.
B. it was discovered, but not invented,
as gamma radiation is naturally
occurring counterpart.
C. it can be controlled by mankind.
D. it can both cause and cure cancer.
E. None of the above
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
3

6. Which electromagnetic radiations carries
the most energy, and is therefore most
penetrating?
A. Microwaves
B. Radiowaves
C. Visible light
D. Gamma rays
E. They all have the same energy.
7. With which statement would the author of
the passage agree?
A. Rigorous experimentation must be
carried out to more accurately asses
damage caused by the diagnostic
use of X-rays.
B. Epidemiologic data from individuals
receiving high doses of radiation can
accurately be interpolated to assess
the effects of low levels of radiation.
C. Non-stochastic effects of radiation
are a more serious problem for
diagnostic radiology than are
stochastic effects.
D. The most effective way to improve
the risk-benefit ratio is to minimize
the number of exposures performed
by using careful radiographs
selection.
E. It is easy to differentiate between
disease caused by exposure to
ionizing radiation and that from other
causes.
8. The beta particle is the same as a(n)
A. neutron.
B. photon of pure energy.
C. proton.
D. helium radical.
E. electron.
9. According to the inverse square law, the
intensity of radiation received is reduced
by a factor of
___ times when a practitioner
stands 4 meters away from a source of
radiation rather than 1 meter.
A. 4
B. 0.25
C. 16
D. 0.06
E. 2
10. The probability of genetic mutation being
caused by low levels of x or gamma
radiation is believed to be
A. stochastic in nature.
B. greater than the risk of cancer.
C. threshold dose related.
D. unrelated to dose.
E. a result of cell death.
11. The principal difficulty encountered when
evaluating the risk of cancer developing
due to the use of diagnostic radiology is
A. inability to distinguish between
disease caused by radiation and that
due to other factors.
B. the relatively long life span of
humans.
C. the size of the population one needs
to follow.
D. the difficulty in obtaining a good
control group.
E. the financial outlay necessary for the
study.
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
4

13. For diagnostic radiology, which statement
is false?
A. Potentially noxious radiations are
employed.
B. This use of X-rays was first
developed very shortly after
Roentgen’s discovery.
C. Particulate radiations are not
employed.
D. Attempts have been made to develop
high yield selection criteria.
E. Such use of X-rays is excluded from
the ALARA Principle as doses are
negligible.
14. Gibbs and his co-workers considered the
risk-benefit ratio for the diagnostic use of
ionizing radiation
A. should be estimated as being
equivalent to that for whole body
exposure to the same radiation level.
B. is complicated by uncertainties in the
definition of the value of a life saved
in units of dose equivalence.
C. can readily be determined by
examining the excess incidence of
cancer an mutations in an irradiated
population.
D. always shows a linear relationships
between risk and the radiation dose.
E. More than one of the above
15. Which electromagnetic radiations travels
at the greatest velocity?
A. X-rays
B. Visible light
C. Radiowaves
D. Microwaves
E. None of these
16. Which statement is true for ionizing
radiation?
A. Certain cancers have been attributed
to radiation injury.
B. Radiation burns are a frequent
complication of the diagnostic use of
x radiation.
C. All levels of ionizing radiation are
known to be dangerous to living
systems.
D. Practitioners adhering to the ALARA
Principle are under no risk from the
use of ionizing radiation.
E. More than one of the above.
17. The paradigm referred to in paragraph 2 is
a(n)
A. precise description for the wave
motion of radiations in the electro-
magnetic spectrum.
B. conceptual model helping to explain
a principal characteristic of electro-
magnetic radiations.
C. explanation for longitudinal wave
motion in the coiled spring.
D. representation of the movement of
physical matter in the electro-
magnetic spectrum.
E. More than one of the above
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
5
12. Of the following, which according to the
text are definitely capable of causing
ionization?
1. Visible light
2. Gamma radiation
3. Microwaves
4. Radiowave radiation
A. All of the above
B. 2, 3 and 4 only
C. 2 only
D. 3 only
E. 4 only

1. Evaluate the expression 5 x 10
-3
x 3 x 10
7
.
A. 1.5 x 10
-10
B. 1.5 x 10
-4
C. 1.5 x 10
4
D. 1.5 x 10
5
E. 1.5 x 10
10
2. The perimeter of a square is 20. Which
represents the area?
A. 5
B. 10
C. 20
D. 25
E. 100
3. What is the approximate value of
A. 1.6
B. 0.16
C. 0.016
D. 0.0016
E. 0.00016
4. Which is the smallest?
A. 11/15
B. 4/5
C. 21/25
D. 5/6
E. 13/17
5. At a certain convention the ratio of men
to women was 3 to 8. If there were 352
people there, how many were men?
A. 32
B. 96
C. 132
D. 220
E. 256
6. If x = and z = , then which is
equal to z?
A. 1/5
B. 4/5
C. 5/4
D. 5/2
E. 5
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
1
Quantitative Reasoning Test Time limit: 45 minutes
QRT – Test Number 51
(An electronic calculator will be available for
the QRT section of the DAT at the test center)

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
2
7. Which is the value of
A. 0.003
B. 0.0003
C. 0.00003
D. 0.000003
E. 0.0000003
A. 1.0
B. 15
C. 33.3
D. 100
E. 340
9. A rectangular room is 3 meters wide, 4
meters long and 2 meters high. How far is
it from the northeast corner at the floor to
the southwest corner at the ceiling?
A. meters
B. meters
C. meters
D. 9 meters
E. 5 meters
10. A person travels to work at an average
speed of 40 mph, and returns home at 60
mph. What, in mph, is the average speed
for the entire trip?
A. 45
B. 46
C. 48
D. 52
E. 54
11. If [b (c + d) + e]a = 135, then which
variable cannot be zero?
A. a
B. b
C. c
D. d
E. e
12. Which is the equation of the line that
contains the point (3, -1) and is
perpendicular to the line y = 3x + 3?
A. y = 3x - 8
B. y = 3x - 10
C. y = (-1/3)x + 2
D. y = (-1/3)x - 2
E. y = (-1/3)x
13. 10 is to 2y as 25x is to
A. 5x.
B. 5xy.
C. 5x/y.
D. x/5y.
E. 5y/x.
14. If 3 liters of 40% orange juice and 1 liter of
50% orange juice are mixed, which is the
percentage of orange juice in the mixture?
A. 90
B. 85
C. 47.5
D. 45
E. 42.5
15. If 2x - 3 > 3x + 7, then which must be
true?
A. x >
B. x > -4
C. x > -10
D. x < -4
E. x < -10
8.

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
3
16. Which represents 5% of 2% of 0.4?
A. 4
B. 0.04
C. 0.004
D. 0.0004
E. 0.00004
17. One pump can fill a vat in 10 minutes.
Another pump can fill the vat in 15
minutes. How many minutes does it take
to fill the vat if both pumps are operating
at the same time?
A. 1/6
B. 6
C. 12
D. 12.5
E. 25
18. If 1 inch equals 2.5 centimeters, then 25
meters equal how many inches?
A. 0.01
B. 0.1
C. 10
D. 62.5
E. 1,000
19. In a given course a student receives
preliminary examination grades of 81, 85,
and 95. The final examination is weighed
for one-third and the average of the
preliminary grades is weighed as 2/3 of
the final grade. What should the final
examination grade be for a semester
average of 90?
A. 99
B. 96
C. 93
D. 88
E. 87
20. If f(z) = 3z
2
- 2z, then f(-1) equals
A. 1.
B. 4.
C. 5.
D. 7.
E. 11.
21. Mary took 9 minutes to walk 3/8 of a mile.
At this rate, how many minutes will it take
to walk the rest of the mile?
A. 11
B. 12
C. 15
D. 18
E. 24
22. What is the distance on a two-dimensional
graph between (7, 6) and (2, -6)?
A. 5
B. 9
C. 13
D. 17
E.
23. In a right triangle ABC with right angle at
C and AB = 6, BC = 3, find AC.
A. 3
B. 6
C. 27
D. 33
E. 3
24. When each of the sides of a square is
increased by 1 yard, the area of the new
square is 53 square yards more than that
of the original square. What is the length
of the sides of the original square?
A. 25
B. 26
C. 27
D. 52
E. 54

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
4
25. A mother’s age is three times her
daughter’s age. In twelve years the
mother’s age will be twice the daughter’s
age at that time. How old is the mother
now?
A. 18
B. 20
C. 24
D. 30
E. 36
26. Find the average of the following list of
three weights: 3 lb. 2oz., 4 lb. 6 oz., and
9 lb. 10 oz.
A. 5 lb. 6 oz.
B. 5 lb. 6 1/3 oz.
C. 5 lb. 11 1/3 oz.
D. 5 lb. 39 1/3 oz.
E. 8 lb. 9 oz.
27. If x = 5, then x + 4 is what percent of
x
2
+ 2?
A. 19
B. 33 1/3
C. 75
D. 300
E. 540
28. Which of the following is the length of the
line segment BC, if AB = 14, AD = 5, and
angle BAD = 30°?
A. 7
B. 9
C. 7
D.
E.
29. A painting which is 4 feet wide and 5 feet
long is surrounded by a rectangular frame
6-inches wide. What percent of the area of
the picture and the frame is occupied by
the frame?
A. 10 1/2
B. 20
C. 30
D. 33 1/3
E. 50
30. A bowl contains 7 green and 3 red
marbles. What is the probability that two
marbles selected at random from this bowl
without replacement are both red?
A. 1/15
B. 9/100
C. 21/100
D. 47/90
E. 3/5

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
5
31. If 1 meter = 3.28 feet, 4/5 of a foot is
approximately what fraction of a meter?
A. 1/5
B. 1/4
C. 1/3
D. 1/2
E. 3/4
32. If y = , then which of the following
represents x?
A. (3y + 2)/(y - 1)
B. (3y + 2)/(y)
C. (3y - 2)/(y + 1)
D. (5y)/(y + 1)
E. (3y - 2)/(y - 1)
33. For all y, the cos y is equal to
A. sin y
B. cos (y + π)
C. sin (-y)
D. sin y + cos y
E. cos (-y)
34. The value of cos (π/3) equals the
value of
A. -cos (2π/3).
B. cos (2π/3).
C. cos (6π/3).
D. -cos (5π/3).
E. cos (4π/3).
35. What is the maximum number of 3-inch
squares (squares that are three inches on
a side) that can be cut from a sheet of tin
19 x 23 inches?
A. 42
B. 48
C. 49
D. 145
E. 146
36. Each of the circles I, II, and III is tangent
to the other two circles. The areas of the
circles are 4π, 9π, and 16π, respectively.
Which represents the length of the
perimeter of the triangle formed by joining
the centers of three circles?
A. 3.0
B. 9.0
C. 14.5
D. 18.0
E. 29.0
37. The numbers (1, 2, 3, 6) have an average
(arithmetic mean) of 3 and a variance of
3.5. What is the average (arithmetic
mean) and variance of the set of numbers
(3, 6, 9, 18)?
A. 9, 31.5
B. 3, 10.5
C. 3, 31.5
D. 6, 7.5
E. 9, 27.5
38. Jill has six different books. She will select
one book on Monday and a different one
to read on Wednesday. In how many ways
can Jill select two different books?
A. 36
B. 30
C. 18
D. 15
E. 12

This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
6
39. A vehicle covers 100 yards in 12.5
seconds. Find the average speed of the
vehicle in feet per second.
A. 2 2/3
B. 4
C. 8
D. 12
E. 24
40.
B. 1/2
C. 1/58
D. 2
E. 58
A.

Dental Admission Preparation Material
Answer Keys
READING COMPREHENSION
1. C
2. E
3. C
4. B
5. D
6. D
7. D
8. E
9. C
10. A
11. A
12. C
13. E
14. B
15. E
16. A
17. B
SURVEY OF THE NATURAL SCIENCES
1. A 26. A 51. C 76. A
2. B 27. E 52. A 77. B
3. D 28. B 53. D 78. E
4. C 29. D 54. A 79. B
5. E 30. C 55. E 80. B
6. C 31. C 56. E 81. C
7. C 32. C 57. C 82. B
8. D 33. A 58. C 83. E
9. B 34. B 59. D 84. A
10. C 35. A 60. A 85. C
11. E 36. A 61. E 86. B
12. A 37. D 62. C 87. C
13. D 38. B 63. B 88. C
14. E 39. B 64. E 89. C
15. A 40. D 65. A 90. C
16. C 41. D 66. C 91. B
17. E 42. A 67. B 92. B
18. B 43. B 68. B 93. C
19. A 44. D 69. E 94. A
20. E 45. D 70. D 95. C
21. D 46. E 71. B 96. D
22. B 47. A 72. D 97. E
23. E 48. B 73. A 98. E
24. E 49. C 74. E 99. B
25. D 50. C 75. A 100. C
QUANTATATIVE REASONING TEST
1. D 15. E 29. D
2. D 16. D 30. A
3. B 17. B 31. B
4. A 18. E 32. A
5. B 19. B 33. E
6. E 20. C 34. A
7. B 21. C 35. A
8. D 22. C 36. D
9. A 23. E 37. A
10. C 24. B 38. B
11. A 25. E 39. E
12. E 26. C 40. C
13. B 27. B
14. E 28. A
PERCEPTUAL ABILITY TEST
1. C 21. A 41. C 61. B 81. B
2. A 22. D 42. B 62. C 82. B
3. B 23. D 43. C 63. C 83. C
4. A 24. A 44. B 64. D 84. D
5. B 25. B 45. A 65. C 85. C
6. D 26. C 46. A 66. B 86. D
7. D 27. C 47. C 67. E 87. A
8. B 28. D 48. C 68. C 88. A
9. C 29. B 49. B 69. E 89. A
10. D 30. B 50. D 70. A 90. B
11. E 31. D 51. A 71. D
12. E 32. C 52. B 72. E
13. D 33. C 53. A 73. B
14. B 34. C 54. B 74. C
15. E 35. A 55. A 75. D
16. B 36. C 56. B 76. B
17. D 37. B 57. A 77. C
18. C 38. B 58. E 78. A
19. A 39. C 59. E 79. D
20. A 40. C 60. D 80. C
This booklet contains copyrighted material and is reprinted with permission. All rights reserved. It may not be reproduced in whole or in part.
