IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
2
Agenda
Network Interface Types and Configuration
Network Settings
Routing Table
Standby Control
Common “Gotchas”

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
3
Shared Interface Settings
IP Configuration Mode:
Static (most common)
•
Manually define IP, static routes, and
gateways.
DHCP
•
Automatic configuration and assignment of
IPv4 address and routing.
SLAAC
•
Automatic configuration and assignment of
IPv6 address and routing.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
4
Shared Interface Settings
Primary IP Address: The IP address in CIDR
format.
Secondary IP Addresses: Any additional IP
addresses to be configured on the interface.
IPv4 and IPv6 default gateways:
The default gateway used to route traffic if no
static route is defined.
The gateway must be in the same subnet as
the primary IP.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
5
Shared Interface Settings
Static Routes:
Provide a route to a specific destination host
range
Multiple Static routes can be configured for an
interface.
The next hop gateway must be in the same
subnet.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
6
Ethernet Interfaces
Machine Types 7199, 7188 & 8436 (Physical):
Refers to the physical interfaces (1g and 10g
interface ports)
Machine Type 5725-T09 (Virtual):
Refers to the configuration of the virtual NICs
on the device (default is 4)
The interface configuration options are the same
for physical and virtual DataPower devices.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
7

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
8
Ethernet Interfaces | Advanced Tab
MAC Address:
Use the NIC's burned-in MAC address by
default.
Users have the ability to use a custom unicast
48-bit hex MAC address, where the first byte
must be even
Physical mode:
Typically use Auto to negotiate to determine
the best speed & duplex.
Manually set the physical mode on both ends
of the link if there is a problem with Auto

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
9
Ethernet Interfaces | Advanced Tab
Offload Processing to Hardware:
By default DataPower offloads TCP/IP
processing of packets to the NIC to improve
performance using Generic Segmentation
Offload (GSO).
IPv6 DAD attempts:
Number of times DataPower will check for
duplicate IPv6 addresses.
IPv6 neighbor discovery delay:
Delay between attempts to determine the link-
layer address of a neighbor on the same (local
link) network, verify the reachability of a
neighbor, and track neighboring devices.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
10

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
11
VLAN Interfaces
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) are logical
Ethernet networks.
There can be several VLANs configured on a
single interface
Frames are modified with a VLAN tag
Switches must be configured to “trunk mode”
in order to use VLAN interfaces
VLANs allow for reduced necessity of phyisical
interface configuration.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
12
[$34540DD2BF17598B.jpg]

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
13
Link Aggregation Interfaces
Benefits of Link Aggregation:
Throughput
•
Both transmit-based and LACP can increase
throughput potential.
•
Transmit-based distributes outgoing traffic
among all links.
•
LACP can use all links for incoming and
outgoing traffic.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
14
Link Aggregation Interfaces
Redundancy
•
Eliminates a common single point of failure,
which is the uplink to a switch.
•
This single point of failure could be caused
by the appliance NIC, the physical cable, or
the switch/switch port. These can all be
eliminated as a single point of failure by
using link aggregation.
•
All 3 types of aggregation can handle
failover of a single interface/link .

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
15
Link Aggregation Interfaces
Aggregation Mode:
Active-backup: One link is active and the other
links are backup. If the active link is lost,
switches to a backup link.
Transmit: A single link for incoming traffic,
distributes outgoing traffic among all links.
LACP: Requires LACP support on switch.
Provides automatic failover and can use the
throughput of all links.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
16
Link Aggregation Interfaces
Ethernet Links:
The list of ethernet interfaces to be used in the
aggregation.
After adding the interface to the aggregation,
the option “enable for link aggregation” must be
on for the ethernet interface.
The ethernet interfaces used can not be part of
another link aggregation or part of a VLAN
interface.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
17
[$34540DD2BF17598B.jpg]

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
18
Network Settings
Block nonmanagement traffic for invalid interface
configuration
New to version 7.0.0 and up
When enabled (recommended) the appliance
will not accept service traffic if there is an
invalid interface configuration.
Disable ICMP
Can disable the appliance responding to ICMP
requests. The specific types are Echo,
Timestamp, Information, and Address Mask.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
19
Network Settings
Disable ECN (default: off): Controls if ECN-capable
sessions are used. ECN is used for communicating
network congestion.
Enable destination-based routing (default: off): This
should only be enabled for backwards compatibility
if necessary. When on, the appliance will respond
to client requests from any interface instead of the
receiving interface.
Relax interface isolation (default: on): Allows
packets to be received as long as the interface
contains an IP in the same subnet.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
20
Network Settings
Disable interface isolation (default: off): When set
to off, packets are only accepted if the destination
is explicitly configured on that interface.
TCP attempts: The number of times a TCP SYN is
retried when there is no response.
ARP attempts: The number of times a failed ARP is
retried.
ARP attempt interval: Number of milliseconds
between ARP attempts.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
21
Network Settings
Enable reverse path filtering (default: off): When
off, the interface accepts packets with a source
address it cannot route. When on, packets with a
non-routable source address are ignored. This
must be off to use standby control.
Enable TCP window scaling (default: on): Allows
window scalling, which can negotiate window sizes
greater than 64 KB.
Starting ephemeral port: The lowest port used for
outbound TCP/UDP connections.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
22
[$34540DD2BF17598B.jpg]

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
23
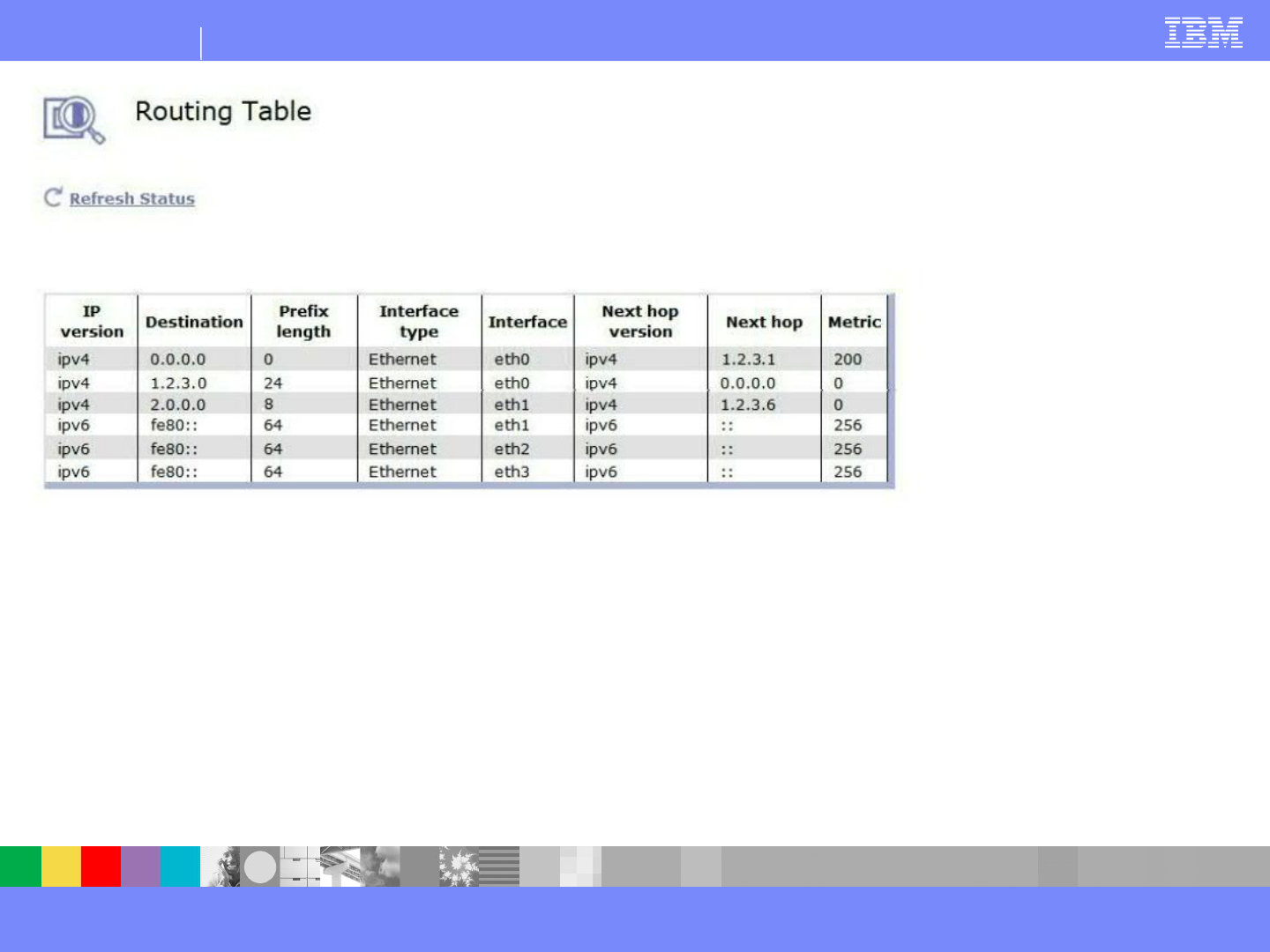
Routing Table
When traffic is bound for a destination IP which is
outside the local network of the configured
interfaces, DataPower will look to the routing table
to determine the next hop.
Routes are pointed to gateways, which act as
access points to traffic entering and exiting the
local network.
Without proper routing, traffic cannot find it's
destination and can cause outages

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
24
Routing Table
If no static route is a match for the destination IP,
DataPower will use the default route.
A static route of '0.0.0.0' is the same as a default
route.
There is a route added automatically for local traffic
which is created automatically when an IP/Subnet is
defined for an interface. Local traffic does not leave
the subnet.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
25
Routing Table
Default Route:
The default route is a “catch-all” route which
typically points to the Internet.
A default route should only be configured if one
exists for the network (check with your
networking team)
There should be one default route configured
for all interfaces on the device.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
26
Routing Table
Static Routes:
Used to route traffic via specific interfaces.
Static routes are matched first based on prefix
length, with 32 being the most specific.
In the case of a tie, the metric is used. The
lower the metric, the higher the priority.
IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
27
[$34540DD2BF17598B.jpg]

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
28
Standby Control
Can be enabled on all interface types (ethernet,
VLAN, and link aggregation).
A standby group is a collection of interfaces on
different appliances which share responsibility for a
single virtual IP (VIP).
As long as one interface from the group is up, the
VIP will accept traffic.
This provides increase failover capabilities and
reduces single points of failure in the topology.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
29
Standby Control
Group Number:
The standby group number in the multicast
domain. This number must be unique per
multicast domain.
Primary virtual IP address:
The IP address used by the active group
member.
Secondary virtual IP addresses:
Additional VIPs which can be used for handling
incoming traffic.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
30
Standby Control
Enable Preemption (default: off):
When preemption is enabled, the highest
priority interface will takeover traffic when it re-
joins the group.
This forces more failovers than necessary and
is recommended to be disabled.
Priority:
Each interface in a group is assigned a priority.
The interface with the highest priority seeks to
be the active member.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
31
Standby Control
Authentication Data:
Used to authenticate if the interface is a
member of the group. All members must use
the same token.
Hello Timer:
The frequency to broadcast hello messages,
which are used to gauge member's status.
Hold Timer:
The duration to wait before attempting failover.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
32
IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
33
Common “Gotchas”
Multiple Default Routes
Can lead to unexpected routing and ultimately
failed connections.
IP Conflicts
Most common when importing a backup from
another environment.
Half-Duplex Physical Mode Setting
Can lead to collisions, resulting in lost
data/packets.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
34
Common “Gotchas”
No static routes or default gateway defined for an
interface
This results in the interface only being able to
communicate with other nodes in the same
subnet.
Simple typos in IPs, subnet masks, and gateways.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
35
Summary
Network Interface Types and Configuration
Ethernet, VLAN, and link aggregation interfaces provide
multiple ways to configure the applaince to handle network
traffic.
Network Settings
There are a lot of appliance wide settings which can be
tweaked. These are generally recommended to be left as the
default unless the change is needed for a specific use case.
Routing Table
The routing table controls how network traffic communication is
handled by the appliance. This relies on static routes and
default gateways to determine the approriate interface to use
for communication.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
36
Summary
Standby Control
DataPower offers standby control, which can provide high
availability and failover at the network interface level between a
group of appliances.
Common “Gotchas”
Ensure your routing table is configured as expected. It is
recommended to work with your network team as there are
likely normal setups depending on your environment.
When exporting/importing configuration ensure that IPs are
changed to prevent duplicate IP conflicts.
Beware of small typos which may not fail when entered, but can
cause unexpected network behavior.

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
38
Connect with us!
1. Get notified on upcoming webcasts
Send an e-mail to wsehelp@us.ibm.com with subject line “wste
subscribe” to get a list of mailing lists and to subscribe
2. Tell us what you want to learn
Send us suggestions for future topics or improvements about our
webcasts to wsehelp@us.ibm.com

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
39
Questions and Answers

IBM Software Group
WebSphere
®
Support Technical Exchange
40
Additional WebSphere Product Resources
Learn about upcoming WebSphere Support Technical Exchange webcasts, and access
previously recorded presentations at:
http://www.ibm.com/software/websphere/support/supp_tech.html
Discover the latest trends in WebSphere Technology and implementation, participate in
technically-focused briefings, webcasts and podcasts at:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/websphere/community/
Join the Global WebSphere Community:
http://www.websphereusergroup.org
Access key product show-me demos and tutorials by visiting IBM Education Assistant:
http://www.ibm.com/software/info/education/assistant
View a webcast replay with step-by-step instructions for using the Service Request (SR)
tool for submitting problems electronically:
http://www.ibm.com/software/websphere/support/d2w.html
Sign up to receive weekly technical My Notifications emails:
http://www.ibm.com/software/support/einfo.html


