2021
Teacher Resource
Guide for
MS Alternate
Academic
Achievement
Standards (MS
AAAS) for
Mathematics
Grades 3-5
Effective Date: 2021-2022 School Year

Page | 2 5-May-21
2021
Teacher Resource Guide for
MS AAAS for
Grades 3-5 Mathematics
Carey M. Wright, Ed.D., State Superintendent of Education
Nathan Oakley, Ph.D., Chief Academic Officer
Robin Lemonis, State Director of Special Education

Page | 3 5-May-21
Mississippi Department of Education
Post Office Box 771
Jackson, Mississippi
39205-0771
Office of Special Education
601.359.3498
https://www.mdek12.org/OSE
The Mississippi State Board of Education, the Mississippi Department of Education, the
Mississippi School for the Arts, the Mississippi School for the Blind, the Mississippi School for the
Deaf, and the Mississippi School for Mathematics and Science do not discriminate on the basis of
race, sex, color, religion, national origin, age, or disability in the provision of educational programs
and services or employment opportunities and benefits. The following office has been designated to
handle inquiries and complaints regarding the nondiscrimination policies of the above-mentioned
entities:
Director, Office of Human Resources
Mississippi Department of Education
Page | 4 5-May-21
Table of Contents
Acknowledgements ............................................................................................................................................ 5
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................................ 7
Support Documents and Resources ................................................................................................................ 7
Structure of the Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Mathematics Grades 3-5 ......................... 8
Teacher Resource Guide for Mathematics Grades 3-5 (Graphic) .............................................................. 9
Levels of Support (LOS) ................................................................................................................................. 10
Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Mathematics Grade 3 ......................................................... 11
Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Mathematics Grade 4 ......................................................... 31
Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Mathematics Grade 5 ......................................................... 68
Page | 5 5-May-21
Acknowledgements
The Mississippi Department of Education gratefully acknowledges the hard work of the following
individuals for their involvement in developing the Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Grades 3-
5: Mathematics.
LaNell Kellum MSU Research and Curriculum Unit
Michelle McKenzie Stone County School District
Amy Rowan Pearl School District
Ginny Sanders MSU Research and Curriculum Unit
Denise Sibley MSU Research and Curriculum Unit
Susan Stampley Senatobia School District
Stacey Todd Ocean Springs School District
Page | 6 5-May-21
The Standards
The 2020 Mississippi Alternate Academic Achievement Standards for Mathematics Grades 3-5 is comprised of
six conceptual categories: number and quantity, algebra, functions, modeling, geometry, and statistics
and probability. The different categories combine to provide a broad scope of the study of
mathematics.
Remaining Material in the Teacher Resource Guide
The remaining materials in the teacher resource guide (performance objectives, real world
connections, vocabulary, and resources) were developed through a collaboration of Mississippi
teachers, administrators, the Mississippi Department of Education (MDE) Office of Special
Education staff, and the Mississippi State University Research and Curriculum Unit staff.
Page | 7 5-May-21
Introduction
The MDE is dedicated to student success, improving student achievement in mathematics and
establishing communication skills within a technological environment. The Mississippi Alternate
Academic Achievement Standards (MS AAAS) provide a consistent, clear understanding of what
students are expected to know and be able to do by the end of each grade level or course. The
purpose of the Alternate Standards is to build a bridge from the content in the general education
mathematics framework to academic expectations for students with the most significant cognitive
disabilities. The standards are designed to be rigorous and relevant to the real world, reflecting the
knowledge and skills that students need for success in postsecondary settings.
Purpose
In an effort to closely align instruction for students with significant cognitive disabilities who are
progressing toward postsecondary settings, the MS AAAS for Mathematics Grades K-8 includes
course-specific standards for mathematics. This document is designed to provide a resource for
kindergarten through eighth grade special education teachers with a basis for curriculum
development and instructional delivery.
The Teacher Resource Guide for Mathematics Grades 3-5 contains prioritized content, which is presented
as a matrix to show the continuum of the concept across complexity levels. The matrix shows
varying access points to the prioritized content. A student’s progression through content contained
in the matrix is intended to be fluid. It is not the intent, nor should it be practice, for a student to be
exposed to content in a straight vertical line through one of the columns. Every student, regardless
of disability, comes to the learning environment with a different set of prior knowledge and
experience. For this reason, a student may be able to access some content from the middle
complexity level and access other concepts at the more complex level. Teachers should evaluate a
student’s ability in relation to the content and select the entry point based on that evaluation.
Students should not be locked into receiving exposure to all content at the same entry point.
Support Documents and Resources
The MDE Office of Special Education aims to provide local districts, schools, and teachers
supporting documents to construct standards-based instruction and lessons, allowing them to
customize content and delivery methods to fit each student’s needs. The teacher resource guide
includes suggested resources, instructional strategies, sample lessons, and activities. Additional
sample activities and resources for selected standards may be added; this shall be a living document
with ongoing updates based on educator feedback. The intent of these resources is to assist teachers
in linking their instruction to the prioritized content. The teacher resource guide includes activity
adaptations for students with a varying range of abilities within the classroom. The activities and
adaptations provided are intended to serve as a model of how students participating in the
Mississippi Academic Assessment Program-Alternate (MAAP-A) may receive academic instruction
in mathematics. There are many ways in which skills and concepts can be incorporated based on
students individual learning styles and needs. Professional development efforts are aligned to the MS
AAAS for Mathematics Grades 3-5 and delivered in accord with teacher resources to help expand
expertise in delivering student-centered lessons.
Page | 8 5-May-21
Structure of the Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Mathematics Grades 3-5
MS AAAS for Mathematics Grades 3-5: A general statement of what students with significant cognitive
disabilities should know and be able to do because of instruction. This guide includes statements
that describe in precise, measurable terms what learners will be able to do at the end of an
instructional sequence; ways educators can link theory to real world activities; focused vocabulary
banks; and additional teaching resources.
• I Can Statement(s): These statements include the Performance Objective(s) as the Most Complex
and scaffolds the performance objectives two additional levels (B) and (C) to Least Complex. This
matrix demonstrates the continuum of the concept across complexity levels. The purpose is to
assist teachers in modifying to meet the unique diverse needs of learners with significant
cognitive disabilities.
• Real World Connections: These items help facilitate learning that is meaningful to students and
prepares them for their professional lives outside of school. When teachers move beyond
textbook or curricular examples and connect content learned in the classroom to real people,
places, and events, students can see a greater relevance to their learning. Real world connections
are used to help students see that learning is not confined to the school, allow them to apply
knowledge and skills in real world situations, and personalize learning to increase and sustain
student engagement.
• Vocabulary: These lists include difficult or unfamiliar words students need to know and
understand.
• Resources: These resources include instructional strategies, lessons, and activities. Additional
sample activities and resources for selected standards may be added; this shall be a living
document with ongoing updates based on educator feedback. The intent of these activities is to
assist teachers in linking their instruction to the prioritized content.
Page | 9 5-May-21
Teacher Resource Guide for Mathematics Grades 3-5 (Graphic)
Vocabulary
Real World Connections
Mississippi Alternate Academic
Achievement Standards for
Mathematics Grades 3-5
Performance Objective(s)
I Can Statements
Resources

Page | 10 5-May-21
Levels of Support (LOS)
Students with significant cognitive disabilities require varying LOS to engage in academic content.
The goal is to move the student along the continuum of assistance toward independence by
decreasing the LOS provided and increasing student accuracy within the context of content to
demonstrate progress.
The following chart describes the continuum of LOS. Appropriate LOS are important to increase
student engagement and student independence and to track student achievement and progress.
Level of
Assistance
Definition Example Non-Example
Non-
Engagement (N)
The student requires assistance
from the teacher to initiate, engage,
or perform; however, the student
actively refuses or is unable to
accept teacher assistance.
The student resists the teacher’s
physical assistance toward the correct
answer.
The student does not look at the
activity.
Physical
Assistance (P)
The student requires physical
contact from the teacher to initiate,
engage, or perform.
The teacher physically moves the
student’s hand to the correct answer.
The teacher taps the correct answer
and expects the student to touch
where he/she tapped.
Gestural
Assistance (G)
The student requires the teacher to
point to the specific answer.
When presenting a choice of three
pictures and asking the student which
picture is a triangle, the teacher will
point to or tap on the correct picture
to prompt the student to indicate
that picture.
The teacher moves the student’s
hand to gesture toward the right
answer.
Verbal
Assistance (V)
The student requires the teacher to
verbally provide the correct answer
to a specific item.
The teacher says, “Remember, the
main character was George. Point to
the picture of the main character.”
The teacher says, “Who is the main
character?” without providing the
information verbally.
Model
Assistance (M)
The student requires the teacher to
model a similar
problem/opportunity and answer
prior to performance.
The teacher models one-to-one
correspondence using manipulatives
and then asks the student to perform a
similar item.
The teacher completes the exact
same activity as the student is
expected to perform.
Independent (I)
The student requires no assistance
to initiate, engage, or perform. The
student may still require other
supports and accommodations to
meaningfully engage in the content
but does not require assistance to
participate and respond.
The teacher asks the student, “Who is
the main character of the book?” and
the student meaningfully responds
without any prompting or assistance.
The teacher asks the student, “Who
is the main character?” and
points to
the picture of the main character.
Page | 11 5-May-21
Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Mathematics Grade 3

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Reason with shapes and their attributes
Page | 12 5-May-21
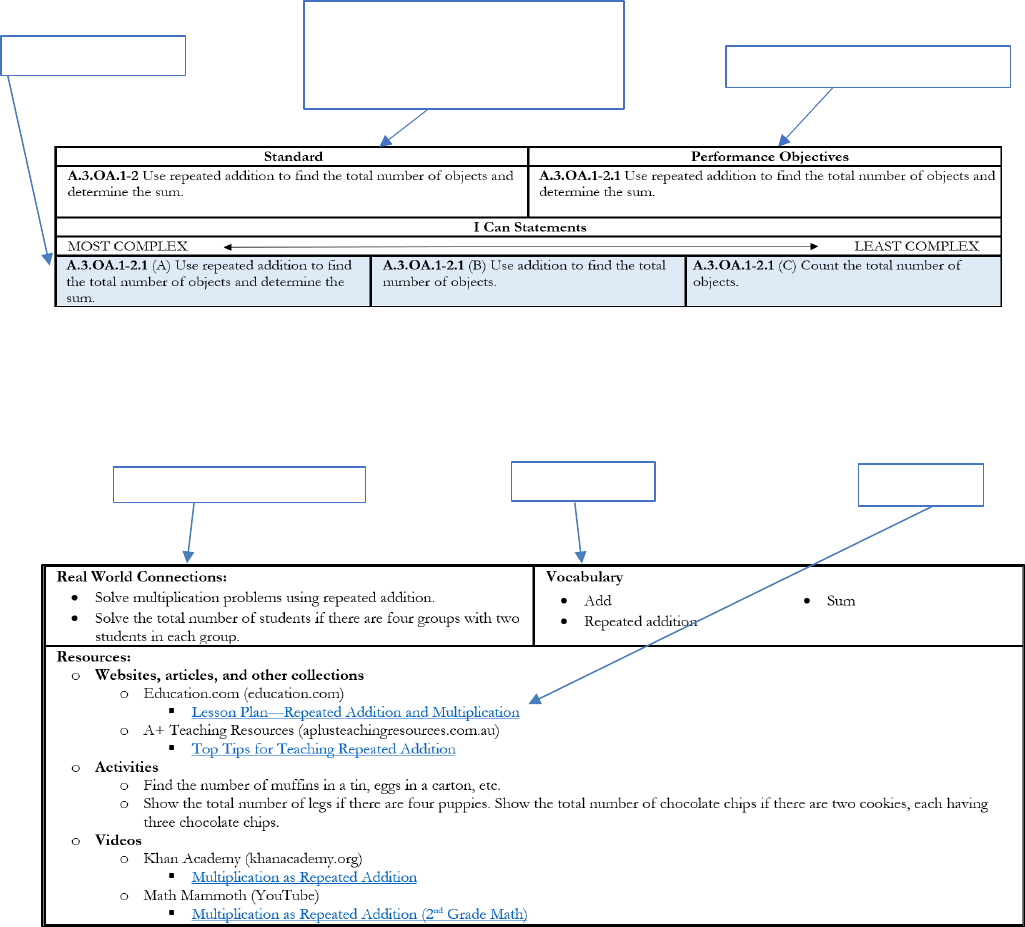
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.OA.1-2 Use repeated addition to find the total number of objects and
determine the sum.
A.3.OA.1-2.1 Use repeated addition to find the total number of objects and
determine the sum.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.OA.1-2.1 (A) Use repeated addition to find
the total number of objects and determine the
sum.
A.3.OA.1-2.1 (B) Use addition to find the total
number of objects.
A.3.OA.1-2.1 (C) Count the total number of
objects.
Real World Connections:
• Solve multiplication problems using repeated addition.
• Solve the total number of students if there are four groups with two
students in each group.
Vocabulary
• Add
• Repeated addition
• Sum
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Education.com (education.com)
Lesson Plan—Repeated Addition and Multiplication
o A+ Teaching Resources (aplusteachingresources.com.au)
Top Tips for Teaching Repeated Addition
o Activities
o Find the number of muffins in a tin, eggs in a carton, etc.
o Show the total number of legs if there are four puppies. Show the total number of chocolate chips if there are two cookies, each having
three chocolate chips.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Multiplication as Repeated Addition
o YouTube by Math Mammoth
Multiplication as Repeated Addition (2
nd
Grade Math)
No alternate standard for 3.OA.3-7

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving the four operations, and identify and explain patterns in arithmetic
Page | 13 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.OA.8 Solve one-step addition or subtraction word problems involving
real-life situations within 20.
A.3.OA.8.1 Solve one-step addition or subtraction word problems involving
real-life situations within 20.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.OA.8.1 (A) Solve one-step addition or
subtraction word problems involving real-life
situations within 20.
A.3.OA.8.1 (B) Solve one-step addition or
subtraction word problems involving real-life
situations within 10.
A.3.OA.8.1 (C) Solve one-step addition or
subtraction problems.
Real World Connections:
• Add items to a grocery cart.
• Pay for items at a store and determine how much money is left.
Vocabulary
• Add
• One-step addition
• One-step subtraction
• Real-life situations
• Word problems
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Iknowit (Iknowit.com)
Addition and Subtraction Word Problems (to 20)
o K5 Learning (k5learning.com)
Add/subtract word problems—mixed word problem worksheets
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Add & Subtract Within 20
o What I Have Learned (whatihavelearnedteaching.com)
5 Tips—How to Teach Students to Solve Word Problems
o Activities
o Subtract within 20 using value blocks.
o Add within 20 using 10 frames.
o Subtract within 20 using a number line.
o Videos
o YouTube by Kids Academy
Teach Addition and Subtraction for Kids—Practice Word Problems
o YouTube by K12 Mojo
Use Addition and Subtraction Within 20 to Solve Word Problems—1OAA1
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Addition and Subtraction Word Problems: Superheroes
No alternate standard for 3.OA.9

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic
Page | 14 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.NBT.1-2 Demonstrate an understanding of place value to the tens
place.
A.3.NBT.1-2.1 Identify place value to the tens place.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.NBT.1-2.1 (A) Identify place value to the
tens place.
A.3.NBT.1-2.1 (B) Use the place value chart to
identify place value to the tens place.
A.3.NBT.1-2.1 (C) Use the place value chart to
identify place value to the ones place.
Real World Connections:
• Count money.
• Recognize numbers and their value in the home, school,
neighborhood, etc.
Vocabulary
• Ones
• Place value
• Tens
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o BrainPOP by FWD Media Inc. (educators.brainpop.com)
Place Value Activities for Kids | Classroom Activities for Teaching Place Value
o Greater Houston Moms (greaterhoustonmoms.com)
45+ Tips & Games for Teaching Place Value
o Teach Starter, Inc. (teachstarter.com)
6 Place Value Games for the Classroom
o Hojo’s Teaching Adventures, LLC (hojoteachingadventures.com)
Teaching Place Value (Great Ideas, Freebies, and More!)
o National Center on Intensive Intervention at American Institutes for Research (intensiveintervention.org)
Teaching Place Value Concepts: Considerations for Instruction
o We Are Teachers (weareteachers.com)
30 Smart Place Value Activities for Elementary Math Students
o Mr. Elementary Math (mrelementarymath.com)
3 Super Tips for Teaching Place Value
o Activities
o Take a walk around the neighborhood. Look for one-, two-, three-digit numbers and have the student read them out loud. You may want
the student to record the numbers he or she sees. Discuss each number and ask how many ones, tens, or hundreds are in the number. Ask
the student to identify the largest and smallest number he or she can find.
o Given the lunch cards for the class and two absent students, subtract two to get the lunch count for the day.
o Using pictures of objects, tally marks, or number cards with numbers to 20, complete an addition or subtraction equation.
o Given 12 counting cubes, count eight more beginning from 12 (e.g., 12, 13, 14, 15, . . . 20).
o Use objects to add by counting (e.g., “I have three apples and get 10 more, how many do I have?” The student counts out three objects

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic
Page | 15 5-May-21
and then counts 10 more to find the total.).
o Given three counting cubes, determine how many more are needed to make six.
o Videos
o YouTube by Kids Academy
Place Value: Ones and Tens | Math for Grade 2 | Kids
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Intro to Place Value
o NUMBEROCK (Numberock.com)
Place Value Song | 1
st
, 2
nd
, & 3
rd
Grade

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic
Page | 16 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.NBT.3 Using vocalization, sign language, augmentive
communication, or assistive technology, count by tens to at least 30 using
models such as objects, base-10 blocks, or money.
A.3.NBT.3.1 Count by tens to at least 30 using models such as objects,
base-10 blocks, or money.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.NBT.3.1 (A) Count by tens to at least 30
using models such as objects, base-10 blocks, or
money.
A.3.NBT.3.1 (B) Count by tens to at least 20
using models such as objects, base-10 blocks, or
money.
A.3.NBT.3.1 (C) Count to 10 using models such
as objects or money.
Real World Connections:
• Count the coins in a piggy bank.
• Sort and count change.
Vocabulary
•
Coins
• Count
• Money
• Objects
•
Tens
• Thirty
• Twenty
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Hand to Mind (hand2mind.com)
Learning About Base-10 Blocks
o Alisal Union School District, Salinas, California (alisal.org)
Grade 2 —Module 3 Place Value, Counting, and Comparison of Numbers to 1,000
o National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (nctm.org)
Base-10 and Place Value NCTM Interactive Institute, 2015
o Keeping My Kiddo Busy Educational Activities for Toddles —Primary Students (keepingmykiddobusy.com)
Kindergarten Math—Teen Numbers and Place Value
o Activities
o Play base-10 riddles to practice place value. Have children build the number with base-10 blocks (draw or write as you give clues. Here are
a few to get you started, then work together to make up some new riddles. I have 23 ones and four tens. Who am I? (63) • I have four
hundreds, 12 tens, and six ones. Who am I? (526) • I have 30 ones and 30 hundreds. Who am I? (3,030) • I am 450. I have 250 ones. How
many tens do I have? (20) • If you put 30 more tens with me, I would be 1,015. Who am I? (715)
o Videos
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Model and Write Numbers Using Base-10 Blocks

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic
Page | 17 5-May-21
o Two Boys and a Dad (twoboysandadad.com)
Ideas on How to Effectively Teach Place Value in a Virtual Setting

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations—Fractions
12
(NF)
CLUSTER: Develop an understanding of fractions as numbers
Page | 18 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.NF.1-3 Differentiate a fractional part from a whole.
A.3.NF.1-3.1 Differentiate a fractional part from a whole.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.NF.1-3.1 (A) Differentiate a fractional part
from a whole.
A.3.NF.1-3.1 (B) Recognize that fractions are
part of a whole.
A.3.NF.1-3.1 (C) Identify a whole.
Real World Connections:
• Put together a puzzle to make a whole.
• Recognize objects in nature that are made up of different parts and,
when combined, make the whole.
• Match halves to assemble them into wholes.
• Build a solid understanding of how parts make up a whole to better
understand addition and subtraction.
Vocabulary
• Differentiate
• Fraction
• Fractional part
• Part
• Whole
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Tales from outside the classroom (talesfromoutsidetheclassroom.com)
Understanding Part-Part-Whole
o Education.com (education.com)
Area: Whole, Parts, and Shapes
o Storyboard That by Clever Prototypes, LLC (storyboardthat.com)
Parts of Wholes or Sets
o Erikson Institute Early Math Collaborative (earlymath.erikson.edu)
A quantity (whole) can be decomposed into equal or unequal parts; the parts can be composed to form the whole.
o Online Math Learning Resources (OnlineMathLearning.com)
Part-Part-Whole Word Problems
o Activities
o Use base-10 blocks to find ways to make a sum. Locking cubes can also be used to practice the same skill. Students explore the related
numbers that are the “parts” that make the “whole.” Have a predetermined number of cubes already separated, or have students grab a
handful and explore the numbers that can be connected to make that number.
o Using a self-sticking, non-adhesive shape, take apart and put together fractional parts of a whole.
o Separate wooden shapes into halves and put them back together to make a whole.
o Identify pictures or objects that are split into fourths.
o Fold a square piece of paper into four equal parts and identify it as four parts of a whole.
o Combine a picture of half an object with the other half to make the whole.

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations—Fractions
12
(NF)
CLUSTER: Develop an understanding of fractions as numbers
Page | 19 5-May-21
o Given a set of pictures, color a half of each whole.
o Assemble four halves into two wholes and state the number of wholes.
o Sort pictures of whole objects and parts into the appropriate category.
o Use a variety of real-world objects (e.g., pizza, segmented chocolate bar, etc.) to demonstrate that each piece represents a part of the whole.
o Shown four halves, assemble them into two wholes.
o Given a puzzle with missing pieces and one that is complete, identify the whole.
o Videos
o Study.com (study.com)
Part to Whole Analogies: Definition & Types
o Nearpod.com (nearpod.com)
Parts of a Whole
o YouTube by Hereford Elementary First Grade
Introduction to Part-Part-Whole
Part-Part-Whole with Missing Part
o YouTube by MooMoo Math and Science
Fraction Basics (Parts of Whole)
o Teachers Pay Teachers (teacherspayteachers.com)
Part-Part-Whole Video Lesson Freebie

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and the estimation of intervals of time, liquid volumes, and masses of objects
Page | 20 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.MD.1 Using vocalization, sign language, augmentive communication,
or assistive technology, tell time to the hour on a digital clock.
A.3.MD.1.1 Tell time to the hour on a digital clock.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.MD.1.1 (A) Tell time to the hour on a digital
clock.
A.3.MD.1.1 (B) Identify which is the hour on a
digital clock.
A.3.MD.1.1 (C) Recognize a digital clock.
Real World Connections:
• Leave for activities on time (e.g., doctor’s appointment, sporting
event, etc.).
• Know when a TV show airs.
• Relate the hour with the time on their daily schedule.
Vocabulary
• Digital clock
• Half-hour
• Hour
• Time
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Teachers Pay Teachers (teacherspayteachers.com) subscription required
Telling Time to the Minute on a Clock Digital Task Cards
o Class Ace (Classace.io)
Learn to Read Digital Clocks
o Education.com (education.com)
Telling Time Games
Telling Time to the Hour
Lesson Plan —Time to Tell Time: Showing and Writing Time
o Activities
o Create a picture gram using pictures of a digital clock to teach students to tell time to the hour.
o Given a time written to the hour, write the digital time.
o Identify the time of a digital clock that is set to the hour.
o Given a time on a digital clock, say the time to the hour.
o Given cards showing digital clocks—one clock having the hour circled and one clock having the minutes circled. Indicate the clock with
the hour circled.
o Given a digital clock and a measuring cup, identify the clock for telling time.
o Videos
o YouTube by Jack Hartmann Kids Music Channel
This Is a Digital Clock | Digital Clock Song for Kids | Telling Time
o YouTube by Claredon Learning

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and the estimation of intervals of time, liquid volumes, and masses of objects
Page | 22 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.MD.2 Identify the appropriate measurement tool for measuring mass
and volume.
A.3.MD.2.1 Identify the appropriate measurement tool for measuring mass
and volume.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.MD.2.1 (A) Identify the appropriate
measurement tool for measuring mass and
volume.
A.3.MD.2.1 (B) Select the appropriate
measurement tool for measuring a liquid.
A.3.MD.2.1 (C) Identify an object that is a solid
and an object that is a liquid.
Real World Connections:
• Select the appropriate tool for measuring water for lemonade.
• Select the appropriate tool for measuring ingredients to cook.
• Measure out the ingredients in a recipe.
• Compare the mass of two items using a two-pan balance scale.
Vocabulary
• Appropriate
• Liquid
• Mass
• Measurement tool
• Volume
• Solid
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Varsity Tutors (Varsitytutors.com)
Choosing Appropriate Units of Measure
o Education.com (education.com)
Measuring Volume
o Class Ace (Classace.io)
Learn About Measuring Tools
o Activities
o Use a weighted scale and balance scales to find out how much objects weigh (mass).
o Given a rock and a glass of water, identify which would be measured using a measuring cup.
o Use a spring scale to measure the weight of objects.
o Place objects from the room into the appropriate measurement category (i.e., solid or liquid).
o Use a measuring cup and have students answer questions about volume measurement conversions.
o When provided a measuring cup and a scale, identify which tool measures liquid.
o Sort real-world items as being measured by grams or liters (e.g., apple measured in grams, juice in liters, etc.).
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Understanding Mass (Grams and Kilograms)
Volume: Intro
Measuring Volume with Unit Cubes

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and the estimation of intervals of time, liquid volumes, and masses of objects
Page | 23 5-May-21
o YouTube by Turtlediary
Science for Kids: Measuring Matter Video
o YouTube by LearnFatafat
Mass and Volume Measurement

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Represent and interpret data
Page | 24 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.MD.3 Use picture or bar graphs to answer questions about data.
A.3.MD.3.1 Use picture or bar graphs to answer questions about data.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.MD.3.1 (A) Use picture or bar graphs to
answer questions about data.
A.3.MD.3.1 (B) Identify the data portrayed in a
picture or bar graph.
A.3.MD.3.1 (C) Recognize a picture or a bar
graph.
Real World Connections:
• Make a picture or bar graph to show the ages of family members.
• Compare data on a bar graph.
• Collect, sort, organize, and graph data of how many different animals
are seen on a nature walk.
• Analyze graphs, answer questions about the data, and make decisions
based on the data.
•
Use a bar graph to show and compare data in different groups.
Vocabulary
• Bar graph
• Data
• Picture graph
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Online Math Learning Resources (OnlineMathLearning.com)
Picture Graphs & Bar Graphs (Grade 2)
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Draw picture graphs to represent data.
Lesson Plan: Understanding data by asking and answering questions based on bar graphs
o FEN Learning Sandbox & Co. (Teachervision.com)
Explaining How to Make a Bar Graph
o Better Lesson (betterlesson.com)
Make Picture Graphs
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Reading Picture Graphs
o Activities
o Ask students to choose their favorite sport and draw a picture graph from the results.
o State how many days were cloudy as charted on a weather chart.
o Use a picture or bar graph to show how many students in the class were identified as wearing blue shirts.
o Using two posters, one for the students with brown shoes and one for the students with blue shoes, place their picture on the poster board

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Represent and interpret data
Page | 25 5-May-21
that indicates what color shoes they have.
o Draw a bar graph with single-unit scale to represent a data set with up to four categories. Solve simple put-together, take-apart, and
compare problems using information presented in a bar graph.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Creating Picture and Bar Graphs
o Lucky Little Learners (luckylittlelearners.com)
Videos That Teach Graphing

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Represent and interpret data
Page | 26 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.MD.4 Measure the length of objects to the nearest whole unit using
standard tools such as rulers, yardsticks, and meter sticks.
A.3.MD.4.1 Measure the length of objects to the nearest whole unit using
standard tools such as rulers, yardsticks, and meter sticks.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.MD.4.1 (A) Measure the length of objects to
the nearest whole unit using standard tools such
as rulers, yardsticks, and meter sticks.
A.3.MD.4.1 (B) Place a standard measuring tool
where one would begin to measure the length of
an object.
A.3.MD.4.1 (C) Identify a ruler as a standard
tool for measuring the length of objects.
Real World Connections:
• Use standard tools to measure items for a building project.
• Use a tape measure to measure wood before cutting.
• Measure items needed to build or construct something.
• Estimate lengths using units of inches, feet, centimeters, and meters.
Vocabulary
• Length
• Standard measuring tools
• Meter sticks
• Whole unit
• Ruler
• Yardstick
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o CK-12 Foundation(ck12.org)
Appropriate Measurement Tools
o Khan Academy (Khanacademy.org)
Common Core Math Skills—Grade 2: Measurement and Data
Practice Measure Lengths (cm, m)
o K5 Learning (k5learning.com)
Measurement Worksheets
o Activities
o Give one ruler length of yarn to each student for a project.
o Measure the length of a row of three tile squares on the floor by repeating a ruler end to end.
o Given a yardstick, measure different lengths or widths of the room and record the measurement.
o When provided two non-standard measuring units, identify the one most appropriate for what is to be measured (e.g., a pencil or long stick
to measure the length of the classroom).
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Measuring Lengths in Different Units
Practice Measuring Length in Different Units
No alternate standard for 3.MD.5-8

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Reason with shapes and their attributes
Page | 27 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.G.1 Use vocalization, sign language, augmentive communication, or
assistive technology to describe the attributes of two-dimensional shapes.
A.3.G.1.1 Describe the attributes of two-dimensional shapes (i.e., number of
sides and angles).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.G.1.1 (A) Describe the attributes of two-
dimensional shapes (i.e., number of sides and
angles).
A.3.G.1.1 (B) Sort shapes by attributes (i.e.,
number of sides and angles).
A.3.G.1.1 (C) Match shapes (i.e., squares,
rectangles, circles, triangles).
Real World Connections:
• Read symbols on maps.
• Sort items based upon attributes.
• Draw pictures using different shapes.
• Design artwork with various shapes.
Vocabulary
• Angle
• Attribute
• Circle
• Hexagon
• Octagon
• Pentagon
• Rectangle
• Sides
• Square
• Triangle
• Two-dimensional shapes
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math Worksheets Land (mathworksheetsland.com)
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Guided Lesson
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Guided Lesson Explanation
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Independent Practice
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Step-by-Step Lesson
o Math 4 Texas Education Service Center Region 11 (Math4texas.org)
Two-Dimensional Shapes
o EasyTeaching (easyteaching.net)
2D Shape Worksheets
o Parenting for the Science Minded by Gwen Dewar, Ph.D. (parentingscience.com)
Tangrams for Kids: Educational Tips and a Printable Tangram Template
o Activities
o Play with flashcards showing the different two-dimensional shapes.
o Play “Guess who?” using shapes.
o Find shapes in real-world areas.
o Videos

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Reason with shapes and their attributes
Page | 28 5-May-21
o Khan Academy (Khanacademy.org)
Recognizing Shapes
o YouTube by Homeschool Pop
2D Shapes for Kids
o YouTube by Icon Math
Angles in Two-Dimensional Figures
o BrainPOP Jr. (jr.brainpop.com)
Plane Shapes
o Investigations 3 Math Words and Ideas (schoolcontent.pk12ls.com)
Geometry—Math Words and Ideas

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 3
rd
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Reason with shapes and their attributes
Page | 29 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.3.G.2 Recognize that shapes can be partitioned into equal areas.
A.3.G.2.1 Recognize that shapes can be partitioned into equal areas.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.3.G.2.1 (A) Recognize that shapes can be
partitioned into equal areas.
A.3.G.2.1 (B) Divide a shape in half (e.g., fold,
draw, cut, etc.)
A.3.G.2.1 (C) Put two halves of a shape together
to make a whole.
Real World Connections:
• Read symbols on maps.
• Sort items based upon attributes.
• Draw pictures using different shapes.
• Design artwork with various shapes.
Vocabulary
• Equal
• Line of symmetry
• Mirror
• Partitioned
• Shapes
• Symmetry
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math Salamanders Limited(math-salamanders.com)
Symmetry Worksheets -Line Symmetry Easier
o Tutoring Hour (tutoringhour.com)
Symmetry Worksheets
o Education.com (education.com)
Lines of Symmetry Resources
o Math Worksheets 4 Kids (mathworksheets4kids.com)
Symmetry Worksheets
o SparkleBox (sparklebox.co.uk)
Symmetry Teaching Resources
o EasyTeaching (easyteaching.net)
Symmetry Worksheets
o Activities
o Use sticky notes and a mirror and have students look for symmetry in letters.
o Use inkblots to show symmetry.
o Videos
o YouTube by Melissa Morey
Symmetry
o YouTube by Periwinkle
Line of Symmetry | Maths for Kids
o YouTube by NUMBEROCK
Page | 31 5-May-21
Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Mathematics Grade 4

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division
Page | 32 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.OA.1-2 Demonstrate the connection between repeated addition and
multiplication.
A.4.OA.1-2.1 Demonstrate the connection between repeated addition and
multiplication.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.OA.1-2.1 (A) Demonstrate the connection
between repeated addition and multiplication.
A.4.OA.1-2.1 (B) Match a picture of repeated
addition to the corresponding multiplication
equation.
A.4.OA.1-2.1 (C) Recognize a multiplication
sign.
Real World Connections:
• Use muffin tins to place manipulatives inside and visually show
arrays.
• Cut an egg carton in half. Have students count each section.
Vocabulary
•
Addition
• Equation
•
Multiplication
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o A+ Teaching Resources (Aplusteachingresources.com.au)
Top Tips for Teaching Repeated Addition
o Education.com (education.com)
Lesson Plan—Repeated Addition and Multiplication
o Khan Academy (Khanacademy.org)
Understand equal groups as multiplication.
Relate repeated addition to multiplication.
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Use repeated addition to find the total number of objects in an array.
o Activities
o Find the number of objects in equal groups using skip counting and repeated addition, then multiply to find the total number in all the
equal groups.
o Show a picture of puppies and try to figure out how many puppies there are by just counting the puppies. Then group the puppies into
equal groupings and count the groupings to help figure out the total number of puppies.
o Videos
o YouTube by SpeedyMind
Multiplication as Repeated Addition | Multiplication for Kids
o YouTube by Math Songs by NUMBEROCK

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division
Page | 33 5-May-21
Equal Groups Multiplication Song | Repeated Addition Using Arrays
o YouTube by MatholiaChannel
Multiplication as Repeated Addition
o Khan Academy (Khanacademy.org)
Multiplication as Repeated Addition

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division
Page | 34 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.OA.3 Solve one-step word problems involving real-life situations using
addition or subtraction within 100 without regrouping.
A.4.OA.3.1 Solve one-step word problems involving real-life situations
using addition or subtraction within 100 without regrouping.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.OA.3.1 (A) Solve one-step addition or
subtraction word problems involving real-life
situations within 100 without regrouping.
A.4.OA.3.1 (B) Solve one-step addition or
subtraction word problems involving real-life
situations within 50 without regrouping.
A.4.OA.3.1 (C) Solve one-step addition or
subtraction word problems involving real-life
situations within 20 without regrouping.
Real World Connections:
• Pay for groceries.
• Count mileage when traveling.
• Recognize professions that involve extensive
addition and subtraction
include bank tellers, accountants, cashiers and food servers and toll
booth operators.
Vocabulary
•
Addition
• Equation
•
Regrouping
• Subtraction
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math Worksheets 4 Kids (mathworksheets4kids.com)
Addition Word Problems Worksheets
Subtraction Word Problem Worksheets
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Unit: Addition and Subtraction
o Autism Classroom Wonderful Workers blog (Mrwinter.com)
Math One-Step Real-World Problems Using Addition & Subtraction Within 20
o Activities
o Use drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent a real-world problem. Use addition and subtraction
within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and
comparing, with unknowns in all positions.
o Ask students to solve a two-step word problem that combines a Put Together (Result Unknown) problem and a Take From (Result
Unknown) problem using marbles in a bag.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Basic Addition

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division
Page | 35 5-May-21
Basic Subtraction
o YouTube by K12 Mojo
Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems—2OAA1.

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Gain familiarity with factors and multiples
Page | 36 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.OA.4 Show how a whole number is a result of two factors.
A.4.OA.4.1 Show how a whole number is a result of two factors.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.OA.4.1 (A) Show how a whole number is a
result of two factors.
A.4.OA.4.1 (B) Identify a factor of a whole
number (e.g., two is a factor of eight because six
can be divided by two exactly three times.)
A.4.OA.4.1 (C) Using manipulatives, divide a
whole number into two equal parts.
Real World Connections:
• Break a graham cracker into two parts, then again into four.
• Equally distribute treats to guests at a birthday party.
Vocabulary
• Divide
• Equal parts
• Factor
• Whole number
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math is Fun by Rod Pierce (Mathsisfun.com)
Factors and Multiples
o Activities
o Do you think that it makes sense to split a day into 24 hours? Would another number have been a better choice? Why or why not?
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Understanding Factor Pairs
Finding Factors of a Number
o YouTube by eHowEducation
How are Whole Numbers Used in Everyday Life?
o YouTube by National Numeracy
Everyday maths! How do we use numbers in everyday life?

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Generate and analyze patterns
Page | 37 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.OA.5 Use repeating patterns to make predictions.
A.4.OA.5.1 Use repeating patterns to predict what comes next in the
pattern.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.OA.5.1 (A) Use repeating patterns to predict
what comes next in the pattern.
A.4.OA.5.1 (B) Continue a pattern with shapes or
numbers when given the rule (e.g., +2, +5,
triangle, circle, etc.).
A.4.OA.5.1 (C) Replicate a pattern with shapes.
Real World Connections:
• Recognize that a
zebra’s back has repeating stripes (black, white, black,
white).
• Repeat colors of beads on a necklace.
• Observe repeating patterns in structures of buildings.
• Help set the table following an appropriate pattern.
Vocabulary
• Pattern
• Prediction
• Repeating
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Education.com (education.com)
Patterns Worksheets and Printables
o Class Ace (Classace.io)
Learn About Repeating Patterns
o NRICH in the Millennium Mathematics Project, University of Cambridge (nrich.maths.org)
Developing Pattern Awareness with Young Children
o Activities
o Focus on repeating patterns and help increase awareness of developing patterns with prompts for considering children’s responses.
o Have students copy patterns and compare their construction with the original pattern.
o Play “spot the mistake” in a pattern and discuss how to repair it.
o Make a sequence with fruit by alternating pears and apples. Make the sequence more complex by adding another type of fruit!
o Collect various leaves and flowers to make patterns, encouraging students to look at the differences between the leaves. The students could
then create patterns using smooth and rough leaves.
o Make a pattern with toy cars Are they going to make a size pattern? A color pattern?
o Encourage students to create sound patterns by making noise with their mouths, clapping, and clicking their fingers. Get into the rhythm!
o Sing songs such as “Head, Shoulders, Knees, and Toes” to learn repeating patterns using parts of the body.
o Videos

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers
Page | 39 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.NBT.2 Compare whole numbers to 10 using symbols (e.g., <, >, =).
A.4.NBT.2.1 Compare whole numbers to 10 using symbols (e.g., <, >, =).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.NBT.2.1 (A) Compare whole numbers to 10
using symbols (e.g., <, >, =).
A.4.NBT.2.1 (B) Identify less than, greater than,
or equal to symbols (i.e., <, >, =).
A.4.NBT.2.1 (C) Compare two quantities to
determine less than, greater than, or equal to.
Real World Connections:
• Compare scores at sporting events.
• Determine which bag has more candy and which has less.
• When given two sets of objects, determine which is more.
•
Compare quantities of candy when shopping.
Vocabulary
• Equal to
• Greater than
• Less than
• Symbols
• Whole numbers
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o BrainPOP by FWD Media Inc. (educators.brainpop.com)
Comparing Numbers Activities for Kids
o Education.com (education.com)
Lesson Plan: Let’s Compare Whole Numbers
o Mrs. Balius: Teaching Resources to Share (mrsbalius.com)
Teaching the Skill of Comparing Numbers
o Activities
o Given two groups of blocks that are close or equal in value, determine which is greater, less, or state they are equal.
o Use a floor number line, have two students stand on two different numbers and determine which is greater or less than.
o State or match meaning of >, <, and = as greater than, less than, or equal to.
o Utilize a number line to compare two numbers greater than 10 and place a card with the correct symbol on the line to show the
relationship (<, >).
o Given two groups of objects, seven blocks and 10 blocks, determine which is greater or which is less.
o Compare scores of a game to determine the winner. Use the symbol to show the relationship between the scores.
o Videos
o Study.com (study.com)
How to Compare Numbers with Math Symbols
o Monterey Institute for Technology and Education, the NROC Project (montereyinstitute.org)
Comparing Whole Numbers
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Comparing Whole Numbers

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers
Page | 41 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.NBT.3 Round any whole number 0-30 to the nearest ten.
A.4.NBT.3.1 Round any whole number 0-30 to the nearest ten.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.NBT.3.1 (A) Round any whole number 0-30
to the nearest ten.
A.4.NBT.3.1 (B) Round ones place numbers,
five and above, to the next 10.
A.4.NBT.3.1 (C) Identify the tens to 30.
Real World Connections:
• Round price of food items on a menu.
• Round number of boys and girls in class to nearest ten.
• Round calendar date to nearest ten.
Vocabulary
• Nearest ten
• Ones place
• Round
• Whole number
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Monterey Institute for Technology and Education, the NROC Project (montereyinstitute.org)
Rounding Whole Numbers
o Basic Mathematics (basic-mathematics.com)
Rounding Whole Numbers
o Education.com (education.com)
Rounding to Whole Numbers Worksheet
o Iknowit (Iknowit.com)
Rounding to the Nearest Ten (Up to 99)
o Activities
o Roll the dice to count up the rounding tape and state the nearest 10.
o Distribute poster boards labeled by tens up to 30 around the room. Give students a number and ask them to go to the nearest 10.
o Using pennies earned, exchange for dimes.
o Using paper plates labeled zero and 10 and a card with a number zero to 10, place the card on the correct plate.
o Use a number line to round to the nearest 10.
o Place fingers on five on a number line and count to find a number greater than five.
o Shown five on a number line, identify a number that is less than five.
o Videos
o YouTube by patrickJMT
Rounding Whole Numbers: Round to the Nearest Ten
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Round Whole Numbers to the Nearest 10 or 100 (3.NBT.A.1)
o YouTube by tenframe

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit whole numbers
Page | 42 5-May-21
Rounding to the Nearest Ten
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Rounding to the Nearest 10
Rounding to the Nearest 10 on the Number Line
o Online Math Learning Resources (OnlineMathLearning.com)
Rounding Numbers

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic
Page | 43 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.NBT.4 Add and subtract two-digit whole numbers.
A.4.NBT.4.1 Add and subtract two-digit whole numbers.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.NBT.4.1 (A) Add and subtract two-digit
whole numbers.
A.4.NBT.4.1 (B) Add and subtract two-digit
whole numbers using a place value chart and
manipulatives.
A.4.NBT.4.1 (C) Add one-digit whole numbers
on a place value chart using manipulatives.
Real World Connections:
• Use addition and subtraction to create and obtain information from
tables, bar graphs, and tally charts.
• Recognize relationships between counting and addition and
subtraction.
Vocabulary
• Add (addition)
• Digits
• Subtract (subtraction)
• Whole numbers
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math 4 Texas Education Service Center Region 11 (Math4texas.org)
Adding Four Two-Digit Numbers & Subtracting Two-Digit Numbers
o What I Have Learned (whatihavelearnedteaching.com)
Models & Strategies for Two-Digit Addition & Subtraction
Two-Digit Addition Activities for Math Stations
o Math-Aids.com (math-aids.com)
Adding and Subtracting 2, 3, or 4 Digit Problems Worksheets
o Activities
o Use counters to add and subtract.
o Produce addends to 10 fluently.
o State 13-1=12 and use magnetic symbols to display the problem.
o Use a sorting box divided into two sections with manipulatives to add, subtract, and regroup to solve addition and subtraction problems.
o Given base-10 pieces, make exchanges to solve multi-digit addition and subtraction problems.
o Use a calculator and show how a problem is solved.
o Use break-apart numbers (e.g., 20+30=50, 3+5=8, 40+8=48).
o Use a number line to demonstrate addition by tens.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Subtracting 2-Digit Numbers Without Regrouping 1
Example: Adding 2-Digit Numbers (No Carrying)

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic
Page | 44 5-May-21
o YouTube by JoAnn’s School
Grade 2 Math 6.4, Using Models to Subtract (2-Digit Numbers)
o YouTube by Math Mammoth
Add and Subtract 2-Digit Numbers Without Regrouping (1st Grade Math)
No alternate standard for 4.NBT.6

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering
Page | 45 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.NF.1-2 Identify models of one half (1/2) and one fourth (1/4).
A.4.NF.1-2.1 Identify models of one half (1/2) and one fourth (1/4).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.NF.1-2.1 (A) Identify models of one half
(1/2) and one fourth (1/4).
A.4.NF.1-2.1 (B)Identify models of one fourth
(1/4).
A.4.NF.1-2.1 (C) Identify models of one half
(1/2).
Real World Connections:
• Complete two- and four-piece puzzles.
Vocabulary
• Fraction
• One fourth
•
One half
• Whole
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o K-5 Math Teaching Resources LLC.(k-5mathteachingresources.com)
Fraction Models
o The Story of Mathematics by Luke Mastin (storyofmathematics.com)
Equivalent Fractions—Explanation & Examples
o JSTOR Digital Library, a part of ITHAKA (Jstor.org)
Engaging Students with Multiple Models of Fractions
o SplashLearn by Studypad, Inc. (splashlearn.com)
Fraction Games for 4
th
Graders
o Pearson Education, Inc. (pearson.com)
Developing Fraction Concepts
o Activities
o Use manipulatives such as rectangular or circular fraction sets, pattern blocks, geoboards and tangrams.
o See how shapes can be partitioned into other shapes using pattern blocks.
o Break plastic eggs in half and put them back to whole.
o Given two squares of paper, one scored for 1/2s and one scored for 1/4s, fold each paper as scored. Unfold the papers and compare to
each other (e.g., 2/4=1/2).
o Given two rectangles, cut one rectangle into half and a second into fourths and compare the rectangles to determine how many fourths
equal a half.
o Using a picture of two circles, cut one in half and the other in fourths and compare them to find how many fourths equal a half.
o Videos
o YouTube by SparklesOnlineSchool

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering
Page | 46 5-May-21
Fractions Part 1—Grade 1 2 3 Mathematics—Whole—Half—Quarter
o Nagwa Limited (Nagwa.com)
Question Video: Identifying One-Half of Circles and Rectangles
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Equivalent Fraction Models

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations – Fractions (NF)
CLUSTER: Build fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understandings of operations on whole numbers.
Page | 47 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.NF.3 Differentiate between whole and half.
A.4.NF.3.1 Differentiate between whole and half.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.NF.3.1 (A) Differentiate between whole and
half.
A.4.NF.3.1 (B) Recognize that two halves make a
whole.
A.4.NF.3.1 (C) Identify a whole.
Real World Connections:
• Measuring ingredients for a recipe.
• Share half of a sandwich.
• Complete two- and four-piece puzzles.
• Practice equal sharing.
• Divide candy into equal shares.
• Explore estimation.
• Grocery shop for a whole chicken or just the parts (e.g., leg, thigh,
tenders, etc.).
• Explore phases of the moon.
Vocabulary
• Differentiate
• Fraction
• Part
• One fourth
• One half
• Whole
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Cpalms (cpalms.org)
Halves and Wholes
Half of This, A Quarter of That, A Whole Lot of Fun!
o SplashLearn by Studypad, Inc. (splashlearn.com)
Halves —Definition with Examples
Fraction Games for 4
th
Graders
o Math-Only-Math.com (math-only-math.com)
Fraction as a Part of a Whole
o K-5 Math Teaching Resources LLC. (k-5mathteachingresources.com)
Fraction Models
o The Story of Mathematics by Luke Mastin (storyofmathematics.com)
Equivalent Fractions—Explanation & Examples
o JSTOR Digital Library, a part of ITHAKA (Jstor.org)
Engaging Students with Multiple Models of Fractions
o Pearson Education, Inc. (pearson.com)

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations – Fractions (NF)
CLUSTER: Build fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understandings of operations on whole numbers.
Page | 48 5-May-21
Developing Fraction Concepts
o Activities
o Given a whole sandwich versus half a sandwich, cut horizontally, vertically, and diagonally and select the whole or half upon request.
o Show the halfway point on a number line.
o Use manipulatives such as rectangular or circular fraction sets, pattern blocks, geoboards, and tangrams.
o See how shapes can be partitioned into other shapes using pattern blocks.
o Break plastic eggs in half and put them back to whole.
o Given two squares of paper, one scored for 1/2s and one scored for 1/4s, fold each paper as scored. Unfold the papers and compare to
each other (e.g., 2/4=1/2).
o Given two rectangles, cut one rectangle into half and a second into fourths and compare the rectangles to determine how many fourths
equal a half.
o Using a picture of two circles, cut one in half and the other in fourths and compare them to find how many fourths equal a half.
o Videos
o YouTube by Skwirk Online Education
Stage 1 Maths—Wholes, Halves and Quarters
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent Fractions and Different Wholes
o YouTube by SparklesOnlineSchool
Fractions Part 1—Grade 1 2 3 Mathematics—Whole—Half—Quarter
o YouTube by Periwinkle
A Whole and a Half | Maths Concepts for Kids | Maths Grade 2
o Nagwa Limited (Nagwa.com)
Question Video: Identifying One-Half of Circles and Rectangles
No alternate standard for 4.NF.4-7

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Page | 49 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.1 Identify the smaller measurement unit that comprises a larger
unit within a measurement system (e.g., inches/foot, centimeter/meter,
minutes/hour).
A.4.MD.1.1 Identify the smaller measurement unit that comprises a larger
unit within a measurement system (e.g., inches/foot, centimeter/meter,
minutes/hour).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.1.1 (A) Identify the smaller measurement
unit that comprises a larger unit within a
measurement system (e.g., inches/foot,
centimeter/meter, minutes/hour).
A.4.MD.1.1 (B) Identify standard units of
measurement (e.g., minutes make up hours,
inches make up a foot, etc.).
A.4.MD.1.1 (C) Given two units of
measurement, identify the smallest unit (e.g., an
inch is smaller than a foot, a minute is smaller
than an hour, etc.).
Real World Connections:
• Select measuring cups and spoons when baking/cooking at home.
• Use units of measurement in daily life. (e.g., A motorist goes to the
gas station and pumps 13 gallons—a measure of volume—into an
automobile. To pay for the gas, the motorist uses dollars—another
unit of measure, economic rather than scientific—in the form of
paper money, a debit card, or a credit card.).
•
Vocabulary
• Larger
• Measurement
• Smaller
• Unit
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Ducksters (ducksters.com)
Kids Math Glossary and Terms: Units of Measurement
o BCcampus Open Publishing Pressbooks (Opentextbc.ca)
Imperial and U.S. Systems of Measurement
o Howard County Public School System, Ellicot City, Maryland
Grade 4 Measurement and Data (4.Md.1) About the Math, Learning Targets, and Rigor
o Activities
o Compare the smallest unit of measurement to the next largest unit of measure using manipulatives (e.g., hour/minute, week/day,
year/month, yard/foot/inch, etc.)
o Select the measurement tool to measure units for weight, length, volume, time, etc.
o Videos
o YouTube by Lucky’s
From Smallest to the Largest Units of Measurement
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Page | 51 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.2.a Tell time using a digital clock. Tell time to the nearest hour
using an analog clock.
A.4.MD.2.a.1 Tell time using a digital clock. Tell time to the nearest hour
using an analog clock.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.2.a.1 (A) Tell time using a digital clock.
Tell time to the nearest hour using an analog
clock.
A.4.MD.2.a.1 (B) Tell time to the nearest hour
using an analog clock.
A.4.MD.2.a.1 (C) Differentiate a digital and
analog clock from other measurement tools as a
tool for telling time.
Real World Connections:
• Make a schedule for planning important activities (e.g., get ready for
school, catch the bus, go to bed, etc.)
• Know when to leave for activities, (e.g., doctor’s appointment,
sporting event, etc.)
• Set a digital clock to set an alarm to get up in the morning.
• Know when a TV show is aired.
Vocabulary
• Analog clock
• Digital clock
• Hour
• Minute
• Time
• Nearest
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Class Ace (Classace.io)
Learn to Read Digital Clocks
o IXL Learning (IXL.com)
2
nd
Grade Math Skills Digital Clock
o Education.com (education.com)
What Time is It—Online Game
Lesson Plan—Time to Tell Time: Showing and Writing Time
o Activities
o Make a clock out of a paper plate.
o Match pictures of digital and analog clocks to each other that represent same time.
o Ask students what the difference is between an analog clock and a digital clock. Ask them which clock is easier to use to tell time and why.
Show the students the digital clock and explain that a digital clock shows the time with numbers. Point to the colon on the clock and
explain that a colon is a punctuation mark used to separate the hours from the minutes in time. Explain to the students that the numbers
on the left of the colon show the hour and the numbers on the right of the colon show the minutes.
o Videos
o YouTube by ChuChu School Learning Videos
Telling Time for Children—Learning the Clock—Digital Clock and Analog Clock

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Page | 52 5-May-21
o YouTube by Maendy Primary
Reading and Understanding Digital Time
o YouTube by Jack Hartmann Kids Music Channel
This Is a Digital Clock | Digital Clock Song for Kids | Telling Time

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Page | 53 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.2.b Measure mass or volume using standard tools.
A.4.MD.2.b.1 Measure mass or volume using standard tools.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.2.b.1 (A) Measure mass or volume using
standard tools.
A.4.MD.2.b.1 (B) Select the appropriate
measurement tool from two related options to
solve problems.
A.4.MD.2.b.1 (C) Identify mass or volume
measurement tools.
Real World Connections:
• Measure ingredients when cooking.
• Measure how much water you drink each day.
• Use a produce scale at the grocery store to estimate the weight of
produce.
• Fill up a vehicle with gas.
• Add the correct amount of liquid laundry detergent to the washing
machine.
Vocabulary
• Mass
• Measure
• Standard tools
• Volume
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o SplashLearn by Studypad, Inc. (splashlearn.com)
Weight and Capacity—Customary Units—Practice
o Varsity Tutors (varsitytutors.com)
Choosing Appropriate Units of Measure
o Class Ace (Classace.io)
Learn About Measuring Tools
o Activities
o Work with units like pounds and gallons or grams and liters to estimate the weight and volume of real-world objects.
o Use liquids, regular solids, and irregular solids to demonstrate that volume is a measure of how much space an object occupies.
o Display standard unit measurement tools and ask students to select the appropriate tool to measure solids, liquids, etc.
o Videos
o YouTube by Region 10 ESC
Measuring Volume
o YouTube by TurtleDiary
Science for Kids: Measuring Video
o TurtleDiary (turtlediary.com)
How to Measure Matter

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Page | 54 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.2.c Use standard measurement to compare lengths of objects.
A.4.MD.2.c.1 Use standard measurement to compare lengths of objects.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.2.c.1 (A) Use standard measurement to
compare lengths of objects.
A.4.MD.2.c.1 (B) Measure the length of objects
using standard tools such as rulers, yardsticks,
and meter sticks.
A.4.MD.2.c.1 (C) Identify items as long or short.
Real World Connections:
• Measure the distance you will travel to visit your family member.
• Measure the height and size of your waste.
• Measure to compare the size of two objects.
• Identify length as an attribute (e.g., That snake is long.).
• Measure seed spacing when planting a garden.
• Measure your growth over time.
• Measure plants to compare growth.
Vocabulary
• Compare
• Length Measure
• Long
• Measure
• Short
• Standard unit
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o janicenovkam.typepad.com
Linear Measurement
o You’ve Got This Math
15 Task Cards to Help Students Practice Length Comparison
o K5 Learning (k5learning.com)
4th Grade Math Worksheets: Measurement
o Activities
o Engage students in experiences that uncover their concept of measurement and use of language. If a student uses the term “big,” model
and encourage the student to identify what is meant and what attribute is being described. Provide materials such as nesting toys for
students to play with when comparing concepts.
o Compare lengths of manipulatives by measuring using a ruler.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Comparing Lengths
o YouTube by MatholiaChannel
Comparing Length

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Page | 55 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.2.d Identify coins (e.g., penny, nickel, dime, quarter) and their
values.
A.4.MD.2.d.1 Identify coins (e.g., penny, nickel, dime, quarter) and their
values.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.2.d.1 (A) Identify coins (e.g., penny,
nickel, dime, quarter) and their values.
A.4.MD.2.d.1 (B) Match a coin to its
corresponding value.
A.4.MD.2.d.1 (C) Select money from other items.
Real World Connections:
• Select the appropriate coins to pay for a good or service.
• Give change in coins to pay for items.
Vocabulary
• Coin
• Dime
•
Nickel
• Quarter
• Half-dollar
•
Value
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o U.S. Mint (usmint.gov)
An Introduction to Coins
o Education.com (education.com)
Identifying Coins
o Activities
o Practice coin identification and sorting coins by type.
o Play store to associate how coins are used in the real world and build an understanding of money in the real world.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.com)
Counting American Coins
o Lucky Little Learners (luckylittlelearners.com)
Videos That Teach Money
o YouTube by Rock ‘N Learn
Learn to Name and Count U.S. Coins
o YouTube by Homeschool Pop
Coins for Kids | Math Learning Video

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Page | 56 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.3 Determine the area of a square or rectangle by counting units
of measurement (e.g., unit squares).
A.4.MD.3.1 Determine the area of a square or rectangle by counting units
of measurement (e.g., unit squares).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.3.1 (A) Determine the area of a square
or rectangle by counting units of measurement
(e.g., unit squares).
A.4.MD.3.1 (B) Show how unit squares can be
used to measure the area of a square or rectangle.
A.4.MD.3.1 (C) Show how unit squares can be
used to measure a square.
Real World Connections:
• Measure the area of a garden.
• Determine the area needed to construct a building.
• Measure to figure out whether a piece of carpet will fit in your
bedroom.
Vocabulary
• Area
• Measure
• Rectangle
• Square
• Unit
• Unit squares
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Common Sense Education(commonsense.org)
Perimeter and Area Real-World Practice
o Class Ace (Classace.io)
Learn About Area
o Education.com (education.com)
Online Game: Alfalfa’s Out of the Box: Perimeter, Area, and Addition
o Activities
o Find the perimeter of a square or rectangle by adding side lengths.
o Count unit squares to find the area of a square or rectangle.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Counting Unit Squares to Find Area Formula
Transitioning from Unit Squares to Area Formula
o YouTube by mathantics
Math Antics—Area
o YouTube by EasyTeaching
An Introduction to Area | Teaching Maths

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Geometric measurement: Understand concepts of angle and measure angles
Page | 57 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.4.a Represent data on a picture or bar graph given a model and a
graph to complete.
A.4.MD.4.a.1 Represent data on a picture or bar graph given a model and a
graph to complete.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.4.a.1 (A) Represent data on a picture or
bar graph given a model and a graph to complete.
A.4.MD.4.a.1 (B) Identify the data that should be
entered on a picture or bar graph given a model.
A.4.MD.4.a.1 (C) Identify the parts of a picture
or bar graph.
Real World Connections:
• Recall how many different animals are seen on a nature walk.
• Show the ages of family members.
Vocabulary
• Bar graph
• Data
• Picture graph
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Better Lesson (betterlesson.com)
Make Picture Graphs
o Education.com (education.com)
Worksheet—Pick a Flower Pictograph
o TeacherVision (teachervision.com)
Explaining How to Make a Bar Graph
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Draw Picture Graphs to Represent Data
o Activities
o Using a bowl of fruit, organize data; create a key, title, and labels; then draw the picture graph.
o Direct students to Think-Pair-Share to explain the purpose of a bar graph portraying animals at the zoo.
o Videos
o YouTube by Freckle by Renaissance
[2.MD.10] Picture and Bar Graphs
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Picture Graphs
Making Picture Graphs and Line Plots
Creating picture and Bar Graphs

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Geometric measurement: Understand concepts of angle and measure angles
Page | 58 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.4.b Using vocalization, sign language, augmentive
communication, or assistive technology, interpret the data from a picture
or bar graph.
A.4.MD.4.b.1 Interpret the data from a picture or bar graph.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.4.b.1 (A) Interpret the data from a
picture or bar graph.
A.4.MD.4.b.1 (B) Identify the data from a
picture or bar graph.
A.4.MD.4.b.1 (C) Identify the parts of a picture
or bar graph.
Real World Connections:
•
Explain the data from a picture graph that shows how many different
animals are seen on a nature walk.
• Describe the ages of family members shown in a bar graph.
• Compare monthly sales at the school store using a bar graph.
•
Describe sports statistics shown in a bar graph.
Vocabulary
• Bar graph
• Data
• Picture graph
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Better Lesson (betterlesson.com)
Make Picture Graphs
Pick a Flower Pictograph
o Education.com (education.com)
Worksheet—Pick a Flower Pictograph
o TeacherVision (teachervision.com)
Explaining How to Make a Bar Graph
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Draw Picture Graphs to Represent Data
o Activities
o Using a bowl of fruit, organize data; create a key, title, and labels; then draw the picture graph.
o Direct students to Think-Pair-Share to explain the purpose of a bar graph portraying animals at the zoo.
o Videos
o YouTube by Freckle by Renaissance
[2.MD.10] Picture and Bar Graphs
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Picture Graphs

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Geometric measurement: Understand concepts of angle and measure angles
Page | 60 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.5 Recognize angles in geometric shapes.
A.4.MD.5.1 Recognize angles in geometric shapes.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.5.1 (A) Recognize angles in geometric
shapes.
A.4.MD.5.1 (B) Identify shapes that contain
angles.
A.4.MD.5.1 (C) Identify an angle.
Real World Connections:
• Notice angles such as in spider webs, the letters in your name, and
building/architecture/construction.
•
Cut a pizza into slices and notice the angles.
Vocabulary
• Angles
• Geometric
• Shapes
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Better Lesson (betterlesson.com)
Angle and line art
o Internet4Classrooms (internet4classrooms.com)
Online Lessons - Recognize angles as geometric shapes that are formed wherever two rays share a common endpoint, and
understand concepts of angle measurement:
o Education.com (education.com)
Worksheet—Shapes with Right Angles
o Activities
o Draw an angular picture of a dog or cat then have students identify each of the angles.
o Draw pictures of stick people and have students find the angles.
o Discuss the angles in a pizza cut into pieces.
o Videos
o YouTube by NUMBEROCK
Angles Song | Acute, Obtuse, & Right Angles | 3
rd
& 4
th
Grade
o EG Videos (egvideos.com)
New York—Grade 4—Math—Measurement and Data—Angles—4.MD.5
o YouTube by Khan Academy
Recognizing Angles | Geometry | 4th Grade
Shapes and Angles

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Geometric measurement: Understand concepts of angle and measure angles
Page | 61 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.MD.6 Identify angles as larger and smaller.
A.4.MD.6.1 Identify angles as larger and smaller.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.MD.6.1 (A) Identify angles as larger and
smaller.
A.4.MD.6.1 (B) Identify a right angle.
A.4.MD.6.1 (C) Identify an angle.
Real World Connections:
• Find angles in nature.
• Find angles in building structures.
•
Find angles in the food you eat.
Vocabulary
• Angle
• Larger
• Right angle
• Smaller
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Education.com (education.com)
Classifying Angles Resources
Lesson Plan—All About Angles
o Helping with Math (helping withmath.com)
Measuring Angles
o Activities
o Once students understand what an angle is, challenge them to find and sort angles (i.e., smaller/larger).
o Set up themed stations around the room with photographs of items (e.g., aquarium, a park, amusement park, a city, the beach, etc.). Make a
worksheet with matching pictures of the photographs for students to use to find and identify angles in the photographs. Provide students
with colored pencils or thin-tipped markers to record the angles on the worksheet’s pictures.
o Videos
o YouTube by Alton Price
Where are the Largest and Smallest Angles in Triangles?
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Identify the Angle
Recognizing Angles
No alternate standard for 4.MD.7

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Draw and identify lines and angles, and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles
Page | 62 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.G.1 Recognize parallel lines and intersecting lines.
A.4.G.1.1 Recognize parallel lines and intersecting lines.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.G.1.1 (A) Recognize parallel lines and
intersecting lines.
A.4.G.1.1 (B) Identify an intersecting line.
A.4.G.1.1 (C) Identify a line.
Real World Connections:
• Read symbols on maps.
• Sort items according to attributes.
• Draw pictures using different shapes.
• Design artwork with various shapes.
Vocabulary
• Intersecting
• Lines
• Parallel
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o K5 Learning (k5learning.com)
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
o DadsWorksheets LLC (dadsworksheets.com)
Basic Geometry: Parallel, Perpendicular, Intersecting
o Tutoring Hour (tutoringhour.com)
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Worksheets
o Common Core Sheets (commoncoresheets.com)
Common Core Sheets—Identifying Lines
o Math Worksheets 4 Kids (mathworksheets4kids.com)
Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines Worksheets
o Class Ace (classace.io)
Learn About Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines
o Activities
o Use a map to show parallel and intersecting lines.
o Find intersecting and parallel lines in the school environment (e.g., sidewalks, concrete walls, etc.).
o Videos
o Online Math Learning Resources (OnlineMathLearning.com)
Pairs of Lines

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Draw and identify lines and angles, and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles
Page | 64 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.G.2 Using vocalization, sign language, augmentive communication, or
assistive technology, describe the defining attributes of two-dimensional
shapes (e.g., number of sides, number of angles).
A.4.G.2.1 Describe the defining attributes of two-dimensional shapes (e.g.,
number of sides, number of angles).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.G.2.1 (A) Describe the defining attributes of
two-dimensional shapes (i.e., number of sides,
number of angles).
A.4.G.2.1 (B) Sort shapes by defining attributes
(i.e., number of sides, number of angles).
A.4.G.2.1 (C) Match shapes (e.g., squares,
rectangles, circles, triangles).
Real World Connections:
• Read symbols on maps.
• Sort items based upon attributes.
• Draw pictures using different shapes.
• Design artwork with various shapes.
• Identify angles in real life.
Vocabulary
• Angles
• Attributes
• Circle
• Hexagon
• Octagon
•
Pentagon
• Rectangle
• Sides
• Square
• Triangle
• Two-dimensional shapes
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math Worksheets Land (mathworksheetsland.com)
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Guided Lesson
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Guided Lesson Explanation
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Independent Practice
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Step-by-Step Lesson
o EasyTeaching (easyteaching.net)
2D Shape Worksheets
Angles Worksheets
o Parentingscience.com
Tangrams for Kids: Educational Tips and a Printable Tangram Template
o Math 4 Texas Education Service Center Region 11 (Math4texas.org)
Two-Dimensional Shapes
o Activities
o Use flashcards to describe the defining attributes of two-dimensional shapes (e.g., number of sides, number of angles).
o Play “Guess who?” using shapes.

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Draw and identify lines and angles, and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles
Page | 66 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.4.G.3 Recognize that lines of symmetry partition shapes into equal
areas.
A.4.G.3.1 Recognize that lines of symmetry partition shapes into equal
areas.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.4.G.3.1 (A) Recognize that lines of symmetry
partition shapes into equal areas.
A.4.G.3.1 (B) Divide a shape into equal halves
(e.g., fold, draw, cut, etc.).
A.4.G.3.1 (C) Put two equal halves of a shape
together to make a whole.
Real World Connections:
• Find lines of symmetry using boundary lines on maps.
• Find lines of symmetry in pictures of buildings.
• Design a play area depicting lines of symmetry with manipulatives.
• Fine the lines of symmetry on highway center stripes.
Vocabulary
• Equal
• Line of symmetry
• Mirror image
• Partitioned
• Shapes
• Symmetry
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math Worksheets 4 Kids (mathworksheets4kids.com)
Symmetry Worksheets
o Education.com (education.com)
Lines of Symmetry Resources
o SparkleBox (sparklebox.co.uk)
Symmetry Teaching Resources
o EasyTeaching (easyteaching.net)
Symmetry Worksheets
o Activities
o Create symmetrical necklaces and bracelets.
o Use sticky notes and a mirror and have students look for symmetry in letters.
o Use inkblots to show symmetry.
o Videos
o YouTube by Melissa Morey
Symmetry
o YouTube by Periwinkle
Line of Symmetry | Maths for Kids
o YouTube by NUMBEROCK
Symmetry Song for Kids | A Day at Symmetry Land | Lines of Symmetry
COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 4
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Draw and identify lines and angles, and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles
Page | 67 5-May-21
Page | 68 5-May-21
Teacher Resource Guide for MS AAAS for Mathematics Grade 5

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA)
CLUSTER: Analyze patterns and relationships
Page | 69 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.OA.3 Identify and extend numerical patterns (e.g., given the rule
“Add 3” and the starting number 0).
A.5.OA.3.1 Identify and extend numerical patterns. (e.g., given the rule
“Add 3” and the starting number 0).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.OA.3.1 (A) Identify and extend numerical
patterns. (e.g., given the rule “Add 3” and the
starting number 0).
A.5.OA.3.1 (B) Extend a numerical pattern.
A.5.OA.3.1 (C) Repeat a numerical pattern.
Real World Connections:
• Make triangles with sticks.
• Notice a tree trunk branching off from one trunk to three branches
to six smaller branches.
•
Set a table with three forks.
Vocabulary
• Add
• Extend
• Pattern
• Repeat
• Sequence
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o The Teacher Studio (theteacherstudio.com)
Teaching Patterns and Patterning in Upper Grades
o Kidskonnect (kidskonnet.com)
How to Teach Kids Number Patterns and Sequences (+5 worksheet bundles to lean on)
o Activities
o Find patterns in printed fabric. Discuss the terms of the patterns.
o Use manipulatives to demonstrate different types of number patterns.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Finding Patterns in Numbers
o YouTube by MsBashforth
Grade 4 Math Lesson on Extending Number Patterns (1.2)
o YouTube by JoAnn’s School
Grade 4 Math 5.6, What are Patterns and Terms?

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Understand the place value system
Page | 70 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.NBT.1 Compare base-10 models up to 99 using symbols (<, >, =).
A.5.NBT.1.1 Compare base-10 models up to 99 using symbols (<, >, =).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.NBT.1.1 (A) Compare base-10 models up to
99 using symbols (<, >, =).
A.5.NBT.1.1 (B) Compare base-10 models up to
50 using symbols (<, >, =).
A.5.NBT.1.1 (C) Identify less than, greater than,
or equal to symbols (<, >, =).
Real World Connections:
• Use dimes and pennies to make connections to place value and
bundling groups of 10.
• Add and subtract using base-10 blocks and models.
• Recognize concrete objects to indicate the number system used (e.g.,
base-10 blocks, rods representing a group of 10, etc.)
•
Compare bags of candy for a party.
Vocabulary
• Base-10
• Equal to
• Greater than
• Less than
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Illustrative Mathematics (Tasks.illustrativemathematics.org)
Using Pictures to Explain Number Comparisons
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Model and Write Numbers Using Base-10 Blocks
o Cortney Ward Jacobs Road Elementary School (learningwardinstruction.wordpress.com)
Place Value
o Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks
GSE First Grade Unit 5: Understanding Place Value
o Hand to Mind (hand2mind.com)
Learning About Base-10 Blocks
o Alisal Union School District, Salinas, California (alisal.org)
Grade 2—Module 3 Place Value, Counting, and Comparison of Numbers to 1,000
o National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (nctm.org)
Base-10 and Place Value NCTM Interactive Institute, 2015
o Keeping My Kiddo Busy Educational Activities for Toddles—Primary Students (keepingmykiddobusy.com)
Kindergarten Math—Teen Numbers and Place Value
o Activities
o Practice place value by collecting objects, placing them on the mat, and bundling when possible.
o Given two numbers, indicate which one is greater or less, or which comes first or last.

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Understand the place value system
Page | 71 5-May-21
o Decompose numbers by place value and compare by tens and ones (e.g., Two 10s and three ones combined is 23 ones.).
o Compose numbers based on place value and compare to another number on the number line.
o Compare two numbers with different numbers in the tens place (e.g., 20 compared to 60 on the number line and explain 20 has two 10s or
20 ones and 60 is made of six 10s or 60 ones as it is written).
o Demonstrate the difference between two numbers using dimes (e.g., 10 compared to 50).
o Compare two numbers on a table of ones and tens.
o Videos
o Mississippi Public Broadcasting Learning Media (mpb.pbslearningmedia.org)
Number & Operations in Base-10
o Khan Academy.(khanacademy.org)
Comparing Multi-Digit Numbers
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Model and Write Numbers Using Base-10 Blocks
o Two Boys and a Dad (twoboysandadad.com)
Ideas on How to Effectively Teach Place Value in a Virtual Setting

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Understand the place value system
Page | 72 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.NBT.2 Use the number of zeros in numbers that are powers of 10 to
determine which values are equal, greater than, or less than.
A.5.NBT.2.1 Use the number of zeros in numbers that are powers of 10 to
determine which values are equal, greater than, or less than.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.NBT.2.1 (A) Use the number of zeros in
numbers that are powers of 10 to determine
which values are equal, greater than, or less than.
A.5.NBT.2.1 (B) Order multiples of 10 in
sequential order of least to greatest (e.g., 10, 100,
1,000, etc.).
A.5.NBT.2.1 (C) Count the zeros in a given
number.
Real World Connections:
• Represent numbers starting with a one and followed by only zeros
(such 10, 100, 1,000, 10,000, etc.) as powers of 10, the result of
multiplying 10 times itself any number of times.
• Extend patterns in the number of zeros when multiplying by the
powers of 10.
•
Keep up with your points for a video game.
Vocabulary
• Values
• Powers of 10
• Number zero
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o John Wiley & Sones. Inc.(dummies.com)
Counting Zeros and Writing Exponents
Exponents and Powers of 10 Patterns
o Duvall County Public Schools, Jacksonville, Florida (dcps.cuvalschools.org)
Lesson 7 Understand Powers of 10
o Activities
o Arrange numbers in order when presented with out of order tens place value number cards.
o Indicate the next correct number in the sequence when presented with numbers 10, 100, __.
o Given 10 dimes, count from 10 to 100 by tens and indicate that is $1.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Introduction to Powers of 10
o YouTube by Math and Science
Multiply by Powers of 10—5th Grade Math

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Understand the place value system
Page | 73 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.NBT.3 Compare whole numbers up to 100 using symbols (<, >, =).
A.5.NBT.3.1 Compare whole numbers up to 100 using symbols (<, >, =).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.NBT.3.1 (A) Compare whole numbers up to
100 using symbols (<, >, =).
A.5.NBT.3.1 (B) Compare whole numbers up to
50 using symbols (<, >, =).
A.5.NBT.3.1 (C) Identify less than, greater than,
or equal to symbols (<, >, =).
Real World Connections:
• Count and compare the coins in your piggy bank.
• Compare Little League scores.
• When using your allowance to buy something, determine if you have
saved enough allowance to make the purchase.
• When shopping for groceries, select the box of with more cherries.
Vocabulary
•
Compare
• Greater than
• Equal to
•
Less than
• Symbols
• Whole numbers
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o HomeSchoolMath.net (homeschoolmath.net)
Which Number is Greater?
o Teachers Pay Teachers (teacherspayteachers.com)—subscription required
Comparing Whole Numbers Using Symbols
o Super Teacher Worksheets (superteacherworksheets.com)
Greater Than/less Than Worksheets
o Activities
o Using a pegboard with pegs placed in the holes divided into two different sets, indicate which has more or less.
o Given two sets of manipulatives, one with five and another with a different number, indicate if second set is more or less than five.
o Given three pennies and five pennies, choose which is more.
o Given a number line, indicate if two or four is closer to five.
o Given a number between one and nine, indicate if the number is closer to zero or 10.
o Using a number line, indicate if given number is closer to zero or 10.
o Videos
o Study.com (study.com)
How to Compare Numbers with Math Symbols

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Understand the place value system
Page | 74 5-May-21
o YouTube by Math & Learning Videos 4 Kids
Comparing Numbers—Greater Than Less Than
o YouTube by Math Songs by NUMBEROCK
Comparing Numbers to 100 Song | Kindergarten-1st Grade
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Comparing Multi-Digit Numbers

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Understand the place value system
Page | 75 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.NBT.4 Round two-digit whole numbers to the nearest 10 from 0-90.
A.5.NBT.4.1 Round two-digit whole numbers to the nearest 10 from 0-90.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.NBT.4.1 (A) Round two-digit whole
numbers to the nearest 10 from 0-90.
A.5.NBT.4.1 (B) Round two-digit whole
numbers to the nearest 10 from 0-50.
A.5.NBT.4.1 (C) Identify 10s to 50.
Real World Connections:
• Round whole numbers to specific place values (e.g., Estimate
the cost
of produce that is $1.25 a pound by rounding its weight
to the nearest
pound.).
• Determine which pizza place is closest to your present location by
rounding the distance.
• Estimate how many people will visit the museum on a given Saturday.
Vocabulary
•
Nearest
• Rounding
• Ones place
•
Two-digit
• Whole number
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math is Fun by Rod Pierce(Mathsisfun.com)
Rounding Numbers
o Monterey Institute for Technology and Education, the NROC Project (montereyinstitute.org)
Rounding Whole Numbers
o Iknowit (Iknowit.com)
Rounding to the Nearest Ten (Up to 99)
o Activities
o Choose the card with the correct answer after being presented a three-digit number and told to round to nearest hundreds place value.
o Given a three-digit number, communicate (i.e., speak, type, etc.) the answer by rounding to the nearest hundreds place value.
o Given a number between 1-89 and cards with the answer on one, pick the correct number when asked to round to nearest 10.
o Using a number line, round to the nearest 10.
o Given a number between one and nine, indicate if the number is closer to zero or 10.
o Using a number line, indicate if a given number is closer to zero or 10.
o Using a pegboard with pegs placed in the holes divided into two different sets, indicate which has more or less.
o Presented two sets, one with five and another with a different number, indicate if second set is more or less than five.

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Understand the place value system
Page | 76 5-May-21
o Presented with three pennies and five pennies, choose which is more.
o Given a number line, indicate if two or four is closer to five.
o Videos
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Round in Real-Life Situations
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Rounding to Nearest 10 and 100
o Cortney Ward Jacobs Road Elementary School (learningwardinstruction.wordpress.com)
Rounding
o Online Math Learning Resources (OnlineMathLearning.com)
Rounding to Tens or Hundreds (Grade 3)

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to the hundredths place
Page | 77 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.NBT.5 Multiply whole numbers up to 5×5.
A.5.NBT.5.1 Multiply whole numbers to 5×5.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.NBT.5.1 (A) Multiply whole numbers up to
5×5.
A.5.NBT.5.1 (B) Use repeated addition to show
multiplication up to 5×5.
A.5.NBT.5.1 (C) Use concrete representations
to show repeated addition up to 5×5.
Real World Connections:
• A recipe calls for 1/3 cup of flour. If you double the recipe, how
much flour do you need?
• You collect one bag of leaves and your friend collected five times as
many bags. How many bags did your friend collect?
• Divide shares of prizes between friends.
• Split up money earned in a group project.
Vocabulary
• Multiply
• Multiplication
• Whole number
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Varsity Tutors (Varsitytutors.com)
Multiplication: Whole Numbers
Common Core: 5th Grade Math: Solve Real-World Problems Involving Multiplication of Fractions and Mixed Numbers:
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NF.B.6 | Study Concepts, Example Questions & Explanations for Common Core: 5th Grade Math
o Tarheelstate Teacher, LLC (tarheelstateteacher.com)
Multiplying Whole Numbers: Ideas for 4th and 5th Grade
o SplashLearn by Studypad, Inc. (splashlearn.com)
Multiplication Games for 5th Graders
o Matific Digital Math Platform (matific.com)
Chapter 2: Multiply Whole Numbers Activities & Worksheets
o Activities
o Create multiplication game boards for two-by-one, three-by-one, four-by-one, two-by-two, and three-by-two digit multiplication.
o When asked what 4×4 equals, identify 16 from an array of choices.
o Add 2+2+2 to justify 2×3.
o Given a picture of a garden with two rows of five carrot plants in each, identify 5+5.
o Given pictures of five cars, arrange them into one row.
o Count four chairs in a row.
o Videos
o YouTube by Math with Mr. J

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to the hundredths place
Page | 78 5-May-21
Multiplying Whole Numbers (Part 2) | 5th Grade Math
o YouTube by TenMarks Amazon
Multiply Whole Numbers: 5.NBT.5
COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to the hundredths place
Page | 79 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.NBT.6-7 Illustrate the concept of division using fair and equal shares.
A.5.NBT.6-7.1 Illustrate the concept of division using fair and equal shares.
(i.e., fold paper in equal shares).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.NBT.6-7.1 (A) Illustrate the concept of
division using fair and equal shares (i.e., fold
paper in equal shares).
A.5.NBT.6-7.1 (B) Construct equal sets.
A.5.NBT.6-7.1 (C) Replicate an equal set from a
model.
Real World Connections:
• Divide up snacks to make sure each friend gets an equal share.
• Count the money earned in a group project and divide it to give each
group member an equal share.
Vocabulary
• Division
• Equal
• Fair
• Illustrate
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Fig Leaf Promotions Limited as Maths No Problem (mathsnoproblem.com)
Exploring the Difference Between Equal Sharing and Equal Grouping in Division
o PBS Kids (pbskids.org)
Fair Sharing
o SplashLearn by Studypad, Inc. (splashlearn.com)
Equal Shares—Definition with Examples
o Parent Homework Help by Laurie Laurendeau (parent-homework-help.com)
Beginning Division: Concept of Equal Sharing
o Activities
o Given a set of three objects, finding a matching set.
o Divide a snack equally among classmates.
o Divide a square piece of paper equally among classmates.
o Given 10 counting cubes divided among three students, recognize when students have the same number (i.e., equal share) and when
students do not have the same number (i.e., unequal share).
o Divide classmates into equal teams.
o Divide a quantity into equal shares (e.g., “If I find $10, how could five people share this?” 10÷5=2 [division structure partitive/fair shares]).
o Use sorting trays and colored blocks to construct equal sets.
o Use an organizer to group or partition objects into two or more sets.
o Create a model of equal sets by counting the objects in each set.
o Videos

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT)
CLUSTER: Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to the hundredths place
Page | 80 5-May-21
YouTube by Learningvids4kids
• How to Share Equally—Introduction to Division
YouTube by Ramy Melhem
•
Dividing by Sharing

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations – Fractions (NF)
CLUSTER: Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions
Page | 81 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.NF.1 Identify models of halves (e.g., 1/2, 2/2) and fourths (e.g., 1/4,
2/4, 3/4, 4/4).
A.5.NF.1.1 Identify models of halves (e.g., 1/2, 2/2) and fourths (e.g., 1/4,
2/4, 3/4, 4/4).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.NF.1.1 (A) Identify models of halves (e.g.,
1/2, 2/2) and fourths (e.g., 1/4, 2/4, 3/4, 4/4).
A.5.NF.1.1 (B) Identify models of 1/4, 2/4, 3/4,
and 4/4.
A.5.NF.1.1 (C) Select the whole and the parts.
Real World Connections:
• Use fractions when measuring lumber to build things.
• Explore fractions in measurements while baking.
• Distribute a pizza between two or four people
• Split a bill while eating at a restaurant.
• Make sure you have enough gas in your tank to make it to your
destination (e.g., 1/2 tank, 1/4 tank).
Vocabulary
• Fourths
• Fractions
• Halves
• Identify
• Part
• Whole
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Rader’s Numbernut.com (numbernut.com)
Finding Fractions Around You
o Smartick University of Oxford (smartick.com)
Learn About Fractions: Halves, Thirds and Fourths
o OK Math and Reading Lady by Cindy Elkins, Educational Consultant (cindyelkins.edublogs.org)
Fractions Part I: Basics K-2
nd
Grade
o Math 4 Texas Education Service Center Region 11 (Math4texas.org)
Understanding Halves and Fourths.
o Activities
o Cut a pizza in half, then fourths, and discuss how two pieces make a whole and four pieces make a whole.
o Explain how you might share half of your hamburger with a friend by dividing it in half.
o Videos
o YouTube by Tuesgray
Fractions in Real Life with Ms. Gray
o YouTube by Boddle Learning
Identify Halves, Thirds, and Fourths—2
nd
Grade Math (2.G.3)
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Number and Operations – Fractions (NF)
CLUSTER: Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions
Page | 83 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.NF.2 Identify models of thirds (e.g., 1/3, 2/3, 3/3) and tenths (e.g.,
1/10, 2/10, 3/10, 4/10, 5/10, 6/10, 7/10, 8/10, 9/10, 10/10).
A.5.NF.2.1 Identify models of thirds (e.g., 1/3, 2/3, 3/3) and tenths (e.g.,
1/10, 2/10, 3/10, 4/10, 5/10, 6/10, 7/10, 8/10, 9/10, 10/10).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.NF.2.1 (A) Identify models of thirds (e.g.,
1/3, 2/3, 3/3) and tenths (e.g., 1/10, 2/10, 3/10,
4/10, 5/10, 6/10, 7/10, 8/10, 9/10, 10/10).
A.5.NF.2.1 (B) Identify models of 1/3, 2/3, 3/3.
A.5.NF.2.1 (C) Recognize that fractions are part
of a whole.
Real World Connections:
• Use fractions when measuring lumber to build things.
• Explore fractions in measurements while baking.
• Distribute a pizza between two or four people
• Split a bill while eating at a restaurant.
• Make sure you have enough gas in your tank to make it to your
destination (e.g., 1/3 tank, 2/3 tank).
Vocabulary
• Fractions
• Identify
• Part
• Thirds
• Whole
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Rader’s Numbernut.com (numbernut.com)
Finding Fractions Around You
o Smartick University of Oxford (smartick.com)
Learn About Fractions: Halves, Thirds, and Fourths
o OK Math and Reading Lady by Cindy Elkins, Educational Consultant (cindyelkins.edublogs.org)
Fractions Part I: Basics K-2
nd
Grade
o Activities
o Cut a pizza into half, then each half into 3 slices, and discuss how two pieces make a whole and six pieces make a whole.
o Explain how you might share a third of your cookie with a friend by dividing it into three equal pieces.
o Videos
o YouTube by Tuesgray
Fractions in Real Life with Ms. Gray
o YouTube by Boddle Learning
Identify Halves, Thirds, and Fourths—2
nd
Grade Math (2.G.3)
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system
Page | 85 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.MD.1.a Tell time using an analog or digital clock to the half or quarter
hour.
A.5.MD.1.a.1 Tell time using an analog or digital clock to the half or
quarter hour.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.MD.1.a.1 (A) Tell time using an analog or
digital clock to the half or quarter hour.
A.5.MD.1.a.1 (B) Tell time to the half hour using
a digital clock and to the half hour using an
analog clock.
A.5.MD.1.a.1 (C) Select the hour represented
using a digital clock (e.g., Point to the clock that
says 3 o’clock.).
Real World Connections:
• Carry out daily routines on time.
•
Know when to get up in the morning, when to go to bed, when to eat
breakfast, lunch, etc.
• Leave for activities on time (e.g., doctor’s appointment, sporting
event, etc.)
•
Know when a TV show is aired.
Vocabulary
• Analog clock
• Digital clock
• Half hour
• Quarter hour
• Time
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Education.com (education.com)
Lesson Plan—Time to Tell Time: Showing and Writing Time
Online Game—What Time is It?
o Class Ace (classace.io)
Learn to Read Digital Clocks
Reading Analog Clocks
o ESL Kidstuff (eslkidstuff.com)
Daily Routines & Times of the Day Lesson Plan
o NRICH in the Millennium Mathematics Project University of Cambridge (nrich.maths.org)
Times of Day
o Activities
o Teach time by the hour, half-hour, and quarter-hour with fun activities (e.g., a clock puzzle, an hour “scoot” game, a time picture sort, etc.).
o Create a picture gram using pictures of a digital clock and an analog clock to teach students to tell time to the hour, half-hour, and quarter-
hour.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Telling Time 1

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system
Page | 86 5-May-21
Telling Time on a Clock
o YouTube by Boodle Learning
How to Tell and Write Time (Digital and Analog Clocks)—1st Grade Math (1.MD.3)

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system
Page | 87 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.MD.1.b Use standard units to measure the weight and length of
objects.
A.5.MD.1.b.1 Use standard units to measure the weight and length of
objects.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.MD.1.b.1 (A) Use standard units to measure
the weight and length of objects.
A.5.MD.1.b.1 (B) Identify standard units of
measurement for weight and length.
A.5.MD.1.b.1 © Identify which tools are used to
measure weight and length.
Real World Connections:
• Use a produce scale at the grocery store.
• Measure distance when taking a road trip.
Vocabulary
• Length
• Measure
• Weight
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Varsity Tutors (Varsitytutors.com)
Choosing Appropriate Units of Measure
o Education.com (education.com)
Measuring Volume
How Much Does It Weigh?
o Class Ace (Classace.io)
Learn About Measuring Tools
o Activities
o Use a weighted scale and balance scales to find out how much objects weigh (mass).
o Use a spring scale to measure the weight of objects.
o Use a ruler to measure the length of manipulatives.
o Use a yardstick to measure the height of a chair.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Understanding Mass (Grams and Kilograms)
o YouTube by Turtlediary
Science for Kids: Measuring Matter Video
o YouTube by LearnFatafat
Mass and Volume Measurement

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system
Page | 88 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.MD.1.c Indicate the relative value of collections of coins.
A.5.MD.1.c.1 Indicate the relative value of collections of coins.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.MD.1.c.1 (A) Indicate the relative value of
collections of coins.
A.5.MD.1.c.1 (B) Identify coins (i.e., penny,
nickel, dime, quarter) and their values.
A.5.MD.1.c.1 (C) Match coins (i.e., penny,
nickel, dime, quarter) that are of equal value.
Real World Connections:
• Learn how to purchase things at a store.
• Select the appropriate coins to pay for a good or service.
• Give change in coins to pay for items.
• Predict how much your club will make selling candy at a sporting
event.
Vocabulary
• Coins
• Collections
• Dime
• Nickle
• Penny
• Quarter
• Value
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o MCK Kentucky Center for Math(kentuckymathmatics.org)
Teaching the Values of Coins
o U.S. Mint (usmint.gov)
An Introduction to Coins
o Education.com (education.com)
Identifying Coins
o Activities
o Practice coin identification and sorting coins by type. Using penny candy, show how many pieces of candy each coin would purchase.
o Play store to associate how coins are used in the real world and build an understanding of money in the real world.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.com)
Counting American Coins
o Lucky Little Learners (luckylittlelearners.com)
Videos That Teach Money
o YouTube by Rock ‘N Learn
Learn to Name and Count U.S. Coins
o YouTube by Homeschool Pop
Coins for Kids | Math Learning Video

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Represent and interpret data.
Page | 89 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.MD.2 Represent and interpret data on a picture, line plot, or bar
graph.
A.5.MD.2.1 Represent and interpret data on a picture, line plot, or bar
graph.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.MD.2.1 (A) Represent and interpret data on a
picture, line plot, or bar graph.
A.5.MD.2.1 (B) Represent data on a picture, line
plot, or bar graph.
A.5.MD.2.1 (C) Identify a picture, line plot, or a
bar graph.
Real World Connections:
• Measure plants for growth comparison.
•
Explain the data from a picture graph that shows how many different
animals are seen on a nature walk.
• Describe the ages of family members shown in a bar graph.
• Compare monthly sales at the school store using a bar graph.
• Describe sports statistics shown in a bar graph.
Vocabulary
• Bar graph
• Data
• Line plot
• Picture graph
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Better Lesson (betterlesson.com)
Make Picture Graphs
Pick a Flower Pictograph
o Education.com (education.com)
Worksheet—Pick a Flower Pictograph
o TeacherVision (teachervision.com)
Explaining How to Make a Bar Graph
o LearnZillion (learnzillion.com)
Draw Picture Graphs to Represent Data
o Activities
o Using a bowl of fruit, organize data; create a key, title, and labels; then draw the picture graph.
o Direct student to Think-Pair-Share to explain the purpose of a bar graph portraying animals at the zoo.
o Videos
o YouTube by Freckle by Renaissance
[2.MD.10] Picture and Bar Graphs

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Geometric measurement: Understand concepts of volume and relate volume to multiplication and to addition
Page | 91 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.MD.3 Identify common three-dimensional shapes (e.g., sphere,
cylinder, cone).
A.5.MD.3.1 Identify common three-dimensional shapes (e.g., sphere,
cylinder, cone).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.MD.3.1 (A) Identify common three-
dimensional shapes (e.g., sphere, cylinder, cone).
A.5.MD.3.1 (B) Identify two or more three-
dimensional shapes (e.g., sphere, cylinder, cone).
A.5.MD.3.1 (C) Identify a sphere.
Real World Connections:
• Identify basic types of three-dimensional shapes to better understand
shape, size, etc. (e.g., basketball, building, flagpole, etc.)
• Observe and spot three-dimensional shapes around you.
• Locate three-dimensional shapes in nature.
• Find shapes in architecture.
Vocabulary
• Cone
• Cylinder
• Three-dimensional
• Shape
• Sphere
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o SplashLearn by Studypad, Inc. (splashlearn.com)
Three-Dimensional Shapes
o BYJU’s (byjus.com)
Three-Dimensional Shapes
o Skills You Need (skillsyouneed.com)
Three-Dimensional Shapes: Polyhedrons, Curved Solids, and Surface Area
o Activities
o Have students observe and spot things around them that have three-dimensional shapes.
o Make a picture graph that shows the various three-dimensional shapes and allow students to list the major characteristics beside each
shape.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Recognizing Shapes
o YouTube by Learning Time Fun
3D Shapes for Kids | 3D Shapes Names | Geometric Shapes | Math for Kids | 3D Shapes
o YouTube by Jack Hartmann Kids Music Channel
3D Shapes Song for Kids | Learn About 3D Shapes

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Measurement and Data (MD)
CLUSTER: Geometric measurement: Understand concepts of volume and relate volume to multiplication and to addition
Page | 92 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.MD.4-5 Determine the volume of a rectangular prism by counting
units of measurement (e.g., unit cubes).
A.5.MD.4-5.1 Determine the volume of a rectangular prism by counting
units of measurement (e.g., unit cubes).
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.MD.4-5.1 (A) Determine the volume of a
rectangular prism by counting units of
measurement (e.g., unit cubes).
A.5.MD.4-5.1 (B) Match rectangular prisms of
the same volume.
A.5.MD.4-5.1 (C) Identify rectangular prisms.
Real World Connections:
• Estimate
how much space you need in a drawer to store certain items.
• Figure out how much space is inside something.
• Build and fill up rectangular garden planters.
Vocabulary
• Prism
• Rectangular
•
Volume
• Unit cube
• Units of measurement
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Education.com (education.com)
Lesson Plan—Volume and Rectangular Prisms
o Math Solutions by Marilyn Burns (mathsolutions.com)
Volume of Rectangular Prisms
o Activities
o Measure a cube using the three dimensions to determine the volume and compare your answer by filling the cube with unit cubes.
o Videos
o YouTube by JoAnn’s School
Grade 5 Math #11.7, Find Volume with Cube Units (Rectangular Prism)
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Volume of a Rectangular Prism

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems
Page | 93 5-May-21
Standard
Performance Objectives
A.5.G.1-4 Sort two-dimensional figures and identify the attributes (e.g.,
angles, number of sides, corners, color) they have in common.
A.5.G.1-4.1 Sort two-dimensional figures and identify the attributes (e.g.,
angles, number of sides, corners, color) they have in common.
I Can Statements
MOST COMPLEX LEAST COMPLEX
A.5.G.1-4.1 (A) Sort two-dimensional figures and
identify the attributes (e.g., angles, number of
sides, corners, color) they have in common.
A.5.G.1-4.1 (B) Sort two-dimensional figures by
attributes (e.g., angles, number of sides, corners,
color) they have in common.
A.5.G.1-4.1 (C) Match two-dimensional figures
with one common attribute (e.g., angles, number
of sides, corners, color).
Real World Connections:
• Match building blocks to assemble a project.
• Sort items in the pantry (e.g., matching colors, shapes, etc.).
• Draw pictures of two-dimensional figures with similar characteristics.
• Use two-dimensional figures to design things.
Vocabulary
• Angles
• Attributes
• Circle
• Hexagon
• Octagon
•
Pentagon
• Rectangle
• Sides
• Square
• Triangle
• Two-dimensional shapes
Resources:
o Websites, articles, and other collections
o Math Worksheets Land (mathworksheetsland.com)
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Guided Lesson
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Guided Lesson Explanation
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Independent Practice
Making Two-Dimensional Shapes—Step-by-Step Lesson
o EasyTeaching (easyteaching.net)
2D Shape Worksheets
Angles Worksheets
o Parentingscience.com
Tangrams for Kids: Educational Tips and a Printable Tangram Template
o Math 4 Texas Education Service Center Region 11 (Math4texas.org)

COURSE: Alternate Mathematics 5
th
Grade
DOMAIN: Geometry (G)
CLUSTER: Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems
Page | 94 5-May-21
Two-Dimensional Shapes
o Activities
o Use flashcards to describe the defining attributes of two-dimensional shapes (e.g., number of sides, number of angles).
o Play “Guess who?” using shapes.
o Find shapes in real world areas.
o Videos
o Khan Academy (khanacademy.org)
Recognizing Shapes











